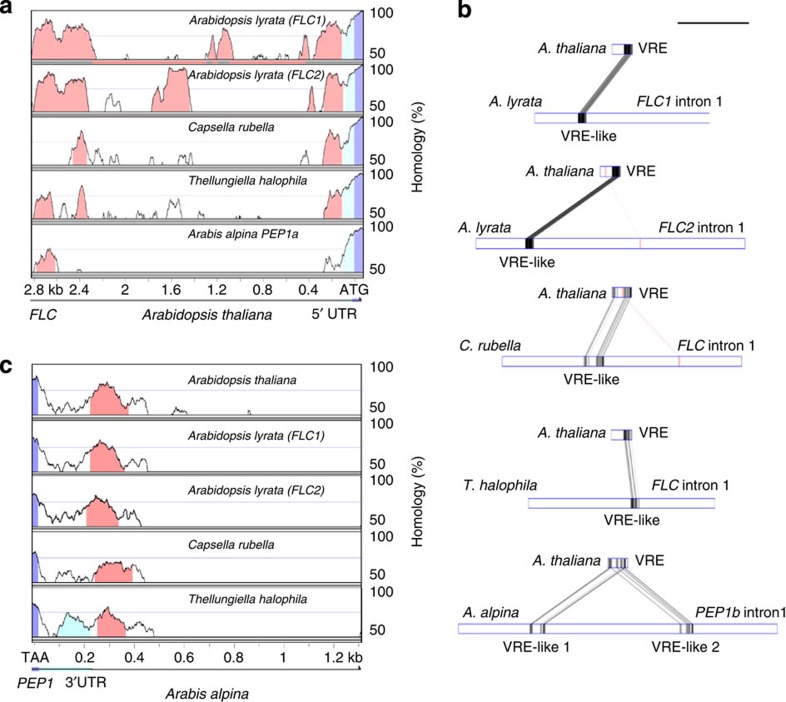
Figure 1. Conservation and divergence of non-coding regulatory cis-elements among FLC orthologues.
(a) mVista pair-wise alignments of the 5′ intergenic regions of FLC orthologues. From top to bottom, A. lyrata FLC1, A. lyrata FLC2, C. rubella FLC, T. halophila FLC and A. alpina PEP1a aligned to A. thaliana FLC. Alignment of PEP1b and A. thaliana FLC is presented in Supplementary Fig. 1f. (b) GATA pair-wise alignment of A. thaliana VRE to the first intron of each of the FLC orthologues mentioned in a. Regions showing homology to the VRE are annotated as VRE-like. For A. alpina PEP1, VRE-like sequences were detected only in the region spanning exon 1b and exon 2 (intron 1 of PEP1b). Scale bar, 1 kb. (c) mVista pair-wise alignment of the 3′ regions of FLC orthologues. PEP1 3′ end was aligned to the 3′ intergenic regions of A. thaliana FLC, A. lyrata FLC1, A. lyrata FLC2, C. rubella and T. halophila FLC orthologues. Coloured areas in mVista graphs illustrate stretches of homology greater than 75% identity at the nucleotide level. Pink, regions of homology in the promoter region (a) or at the 3′ end (c); dark blue, exonic sequences; light blue, untranslated region. Grey and pink boxes in GATA plots are homologous regions and inverted homologous regions respectively (the darker the box, the higher the similarity).