Figure 2. Functional association of Mediator and activating ncRNAs.
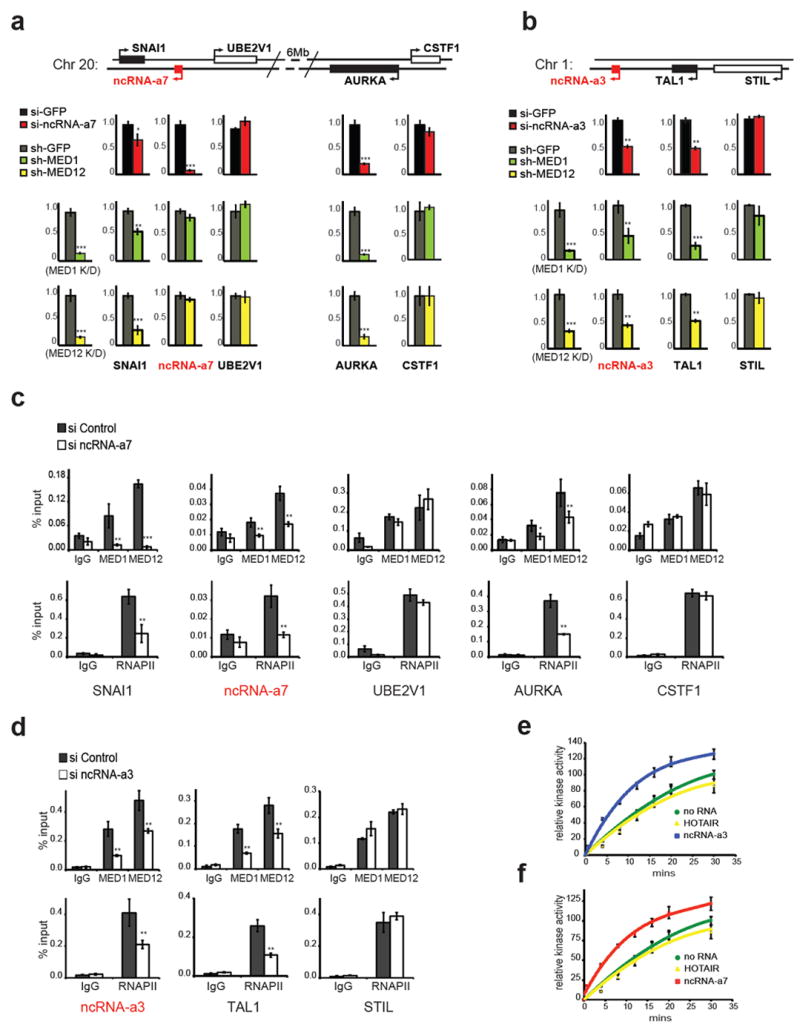
a, Knockdowns of ncRNA-a7 or Mediator subunits decrease SNAI1, AURKA expression. Depletion of ncRNA-a7 diminished SNAI1 and AURKA expression by Real-time PCR (top red bars). Similarly knockdowns of MED1 (green bars) or MED12 (yellow bars) reduce SNAI1 or AURKA expression.
b, Knockdowns of ncRNA-a3 or Mediator subunits decrease TAL1 expression. Expression of TAL1 or control STIL following knockdowns of ncRNA-a3 (red bars), MED1 (green bars) and MED12 (yellow bars) are shown.
c-d, Knockdowns of ncRNA-a7 (c) or ncRNA-a3 (d) reduce the genomic occupancy of MED1, MED12 (top panels) or RNAPII (bottom panels) on SNAI1, AURKA (c) or TAL1 (d) in A549 cells.
e-f, Activating ncRNAs specifically stimulate Mediator kinase activity toward histone H3.1 substrate in vitro. Quantification of kinase assay following addition of ncRNA-a7 (e) or ncRNA-a3 (f). Error bars represent ±SEM (n=3), p<0.01 by two-tailed Student’s T-test.
The mean ±SEM for all results represent three independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by two-tailed Student’s T-test.
