Figure 4. Mediator complex and ncRNA-as promote chromatin looping.
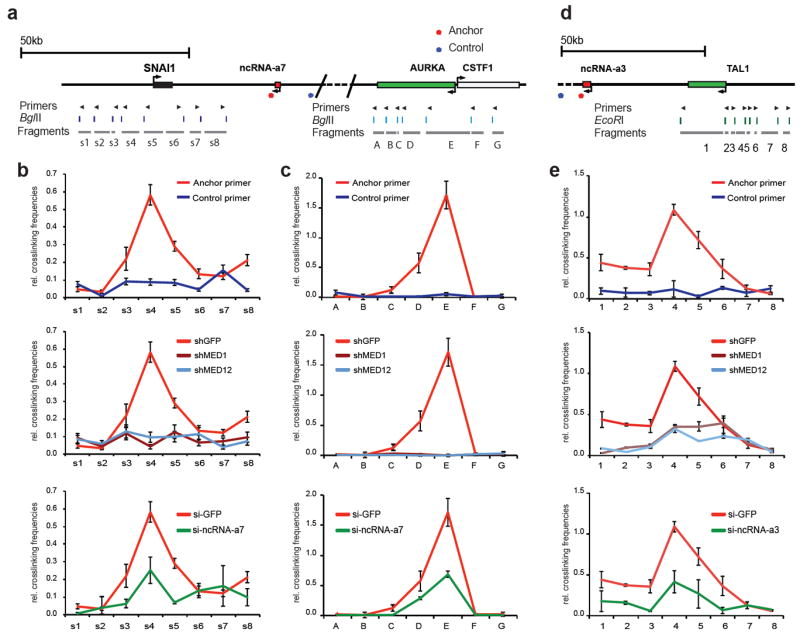
The schematic diagrams represent the genomic locus between the ncRNA-a7, SNAI1 and AURKA loci (a), the ncRNA-a3 and TAL1 (d). The top arrows show the position of primers, the digestion sites are shown in the middle and the s1-8, A-G or 1-8 fragments are presented below.
The looping events between ncRNAs and its targets were detected between ncRNA-a7 and SNAI1 (b), ncRNA-a7 and Aurka (c) and ncRNA-a3 and TAL1(e) using chromosome conformation capture (3C). Depletion of MED1 or MED12 abolished the loop interaction (b,c,e, middle panels). Knockdown of ncRNA-a7 or ncRNA-a3 reduced the chromosomal looping events (b,c,e, lower panels). The interaction frequency between the anchoring points and distal fragments were determined by Real-time PCR and normalized to BAC templates and control anchors. Each error bar represents ±SEM from three independent experiments, p<0.01 by two-tailed Student’s T-test. Representative gel images of the 3C experiments for AURKA are presented in Supplementary Figure 3.
