Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the structures of mammalian Kv α- and β-subunits comprising voltage-gated K+ channels of the Shaker-related subfamily.
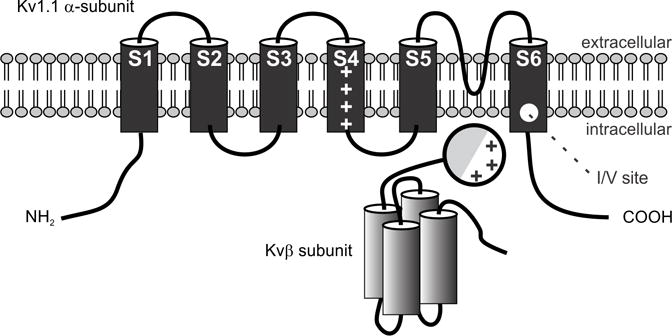
Shown is the proposed topology for α-subunits expressing non-inactivating K-channels and a possible topology for Kvβ1 which contains four α-helices and an amino terminal inactivating ball domain with lipophilic (shaded) and charged regions. This domain swings upon depolarization into the pore and causes rapid inactivation of the channel. The position of the transmembrane voltage sensor (S4), the K+ ion selectivity filter (S5–S6 linker) and the I/V editing site in the α-subunit are indicated (Adapted from Heinemann, 1994).
