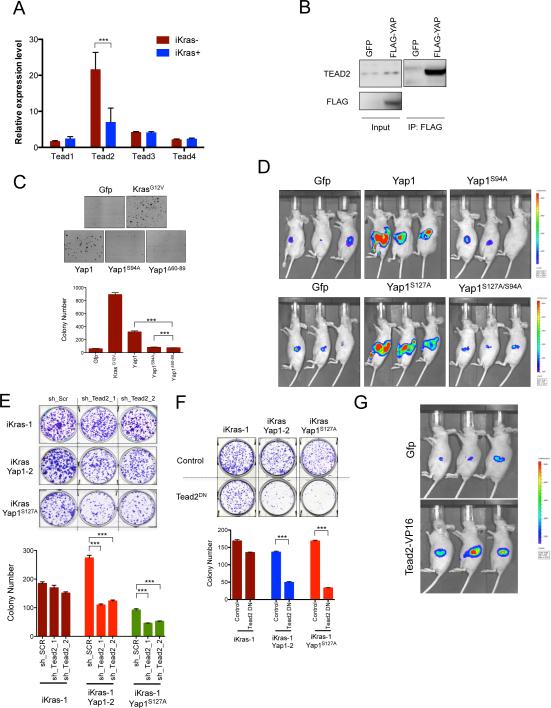
Figure 4. Interaction of Yap1 with Tead2 is critical for it's ability to bypass KrasG12D- dependence.
(A) qRT-PCR for expression of Tead family of transcription factors (Tead1-4) in iKras− and iKras+ relapse tumors. Error bars represent SD of the mean, ***p < 0.001. (B) Tead2 interacts with Yap1 in Yap1 (Flag-tagged) expressing cells (described in 3C). Input (25%) is used as a reference. (C) Sustained expression of wild-type Yap1 but not TEAD binding defective Yap1 mutants (YapS94A and Yap1Δ60-89) can promote anchorage independent growth of iKras cells offdoxy. For each condition, five random fields were counted. Error bars represent SD of the mean, ***p < 0.001. (D) Mutation in Tead binding domain of Yap1 (S94A) dramatically decreases the ability of Yap1 or Yap1S127A to substitute for oncogenic Kras in vivo. Representative images shown at 6 weeks off-doxy (n=5 per group). (E) Representative wells (top) of the clonogenic growth assay upon knockdown of Tead2 by two independent shRNAs in Yap1 (or Yap1S127A) expressing cells (described in 3C). Quantification of cell growth is shown below. Error bars represent SD of triplicate wells, ***p < 0.001. (F) Dominant negative Tead2 (Tead2DN) selectively suppresses proliferation of Yap1 (or Yap1S127A) expressing cells but not the KrasG12D expressing iKras cells. Quantification of cell growth is shown below. Error bars represent SD of triplicate wells, ***p < 0.001. (G) Transcriptionally active form of Tead2 (Tead2-VP16) can substitute oncogenic Kras for in vivo tumor growth. Representative images are shown at 6 weeks off-doxy (n=5 per group).
See also Figure S4.