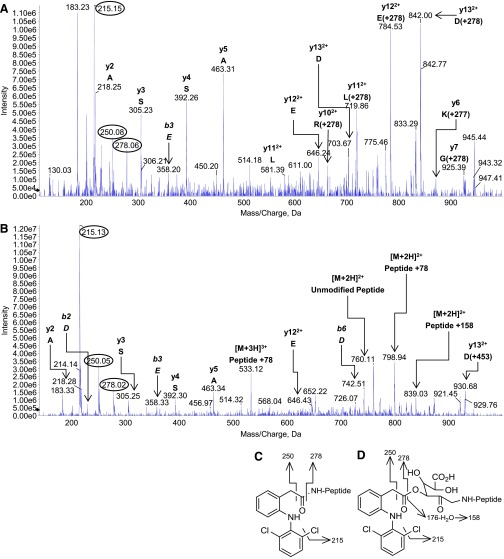
Fig. 4.
Product-ion spectra of modified HSA peptide 182LDELRDEGKASSAK195 acquired during LC-MS/MS analysis of a tryptic digest of protein reacted in vitro with synthetic diclofenac 1β-AG (50:1 molar ratio of AG:HSA). (A) The diclofenac-acylated peptide (peptide + 277 amu; parent ion, [M + 3H]3+ at m/z 599.2). (B) The glycated peptide (peptide + 453 amu; incorporating glucuronyl and drug carboxyl residues; parent ion, [M + 3H]3+ at m/z 658.6). The MRM survey scans were set up to search for acylated and glycated HSA peptides with missed trypsin cleavages, i.e., covalent modifications, at lysine residues. The m/z values of the modified peptides and fragments correspond to the 35Cl2 isobars. The y6 ion of the acylated peptide (m/z 868) was adducted (+277 amu, the diclofenac acyl residue) at Lys190. The glycated peptide did not yield any observable y or b ions bearing the complete glycation structure. The multiply charged peptide + 158 amu ion was assigned to a whole-peptide species that retained the dehydrated residue of the dehydroglucuronic acid moiety. The acylated peptide’s parent ion also yielded peptide fragments that had undergone collision-induced elimination of the entire adduct residue. Fragment ions of the adducts are circled. The principal adduct-derived fragment ions of the modified peptide were rationalized as shown. (C) Fragment ions of the acyl adduct. (D) Fragment ions of the glycation adduct.