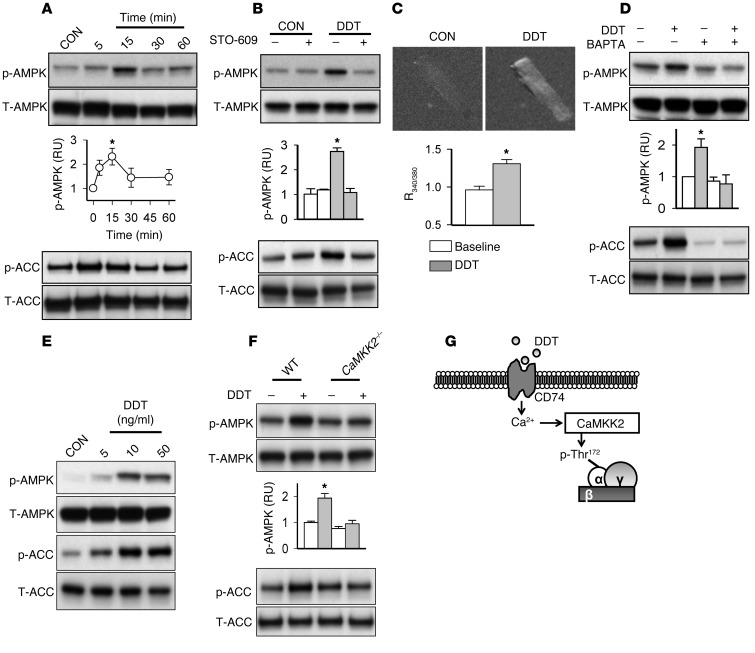
Figure 4. DDT activates AMPK through a CaMKK-dependent mechanism.
(A) Time-dependent activation of the AMPK pathway in adult rat adult ventricular cardiomyocytes treated with recombinant DDT (400 ng/ml). (B) Effect of the CaMKK inhibitor STO-609 (2 εM) on rDDT-induced AMPK activation in cardiomyocytes. (C) Intracellular calcium imaging was performed with fura-2-acetoxymethyl ester (2 εM) in rat cardiomyocytes incubated without (baseline) or with rDDT (400 ng/ml). Original magnification, ×20. The ratio of 340 nm to 380 nm fluorescence intensity [R(340/380)] was recorded as a relative measure of intracellular calcium concentration. (D) Effect of binding intracellular calcium with BAPTA-AM (10 εM) on rDDT stimulation of AMPK phosphorylation in cardiomyocytes. (E) WT mouse hearts were perfused with and without rDDT (5–50 ng/ml) for 15 minutes, and phospho- and total AMPK and ACC were assessed in immunoblots of heart homogenates. (F) DDT perfusion was also performed in Camkk2–/– hearts, and phospho- and total AMPK and ACC were subsequently assessed. (G) DDT activates AMPK through a Ca2+/CaMKK-dependent pathway. p-Thr172, phosphorylation of AMPK at the Thr172 activating site in the catalytic domain. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4–6 per group. *P < 0.05 vs. respective control.