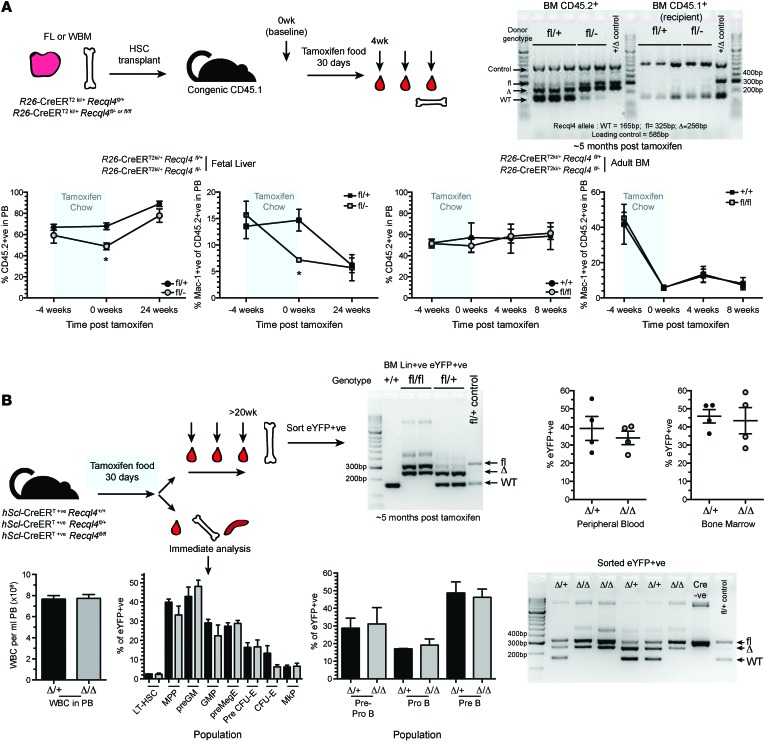
Figure 6. Profound selection against Recql4 deletion in HSCs.
(A) Fetal liver or whole BM was isolated from donors of the indicated genotypes and transplanted into irradiated CD45.1 recipients. Hematopoiesis was allowed to establish for 5 weeks; then chimerism was assessed (4-week time point). Recipients were then placed on tamoxifen food for 30 days. PB was serially monitored at the indicated times, and total chimerism (CD45.2+ve) and myeloid chimerism (Mac-1+ve) are shown from each independent experiment. At end point, CD45.2 cells were isolated from the BM and genomic PCR performed to determine RECQL4 status;data shown are representative genotyping results from 1 of the experiments; n = 5 recipients/genotype/experiment. (B) hScl-CreERT R26eYFP Recql4 mice of the indicated genotypes were fed tamoxifen diet for 30 days. One cohort was left for long-term observation (upper panels). At end point, eYFP+ve cells were isolated from the BM and genomic PCR performed to assess Recql4 status; the percentage of eYFP was assessed in the PB and BM. A second cohort was analyzed at the end of the 30-day feeding of tamoxifen. Femur cellularity, contribution of eYFP+ve cells to each phenotypic population, and genomic PCR were performed. n > 3 per genotype per experiment. Data expressed as mean ± SEM, Student’s t test. *P < 0.05.