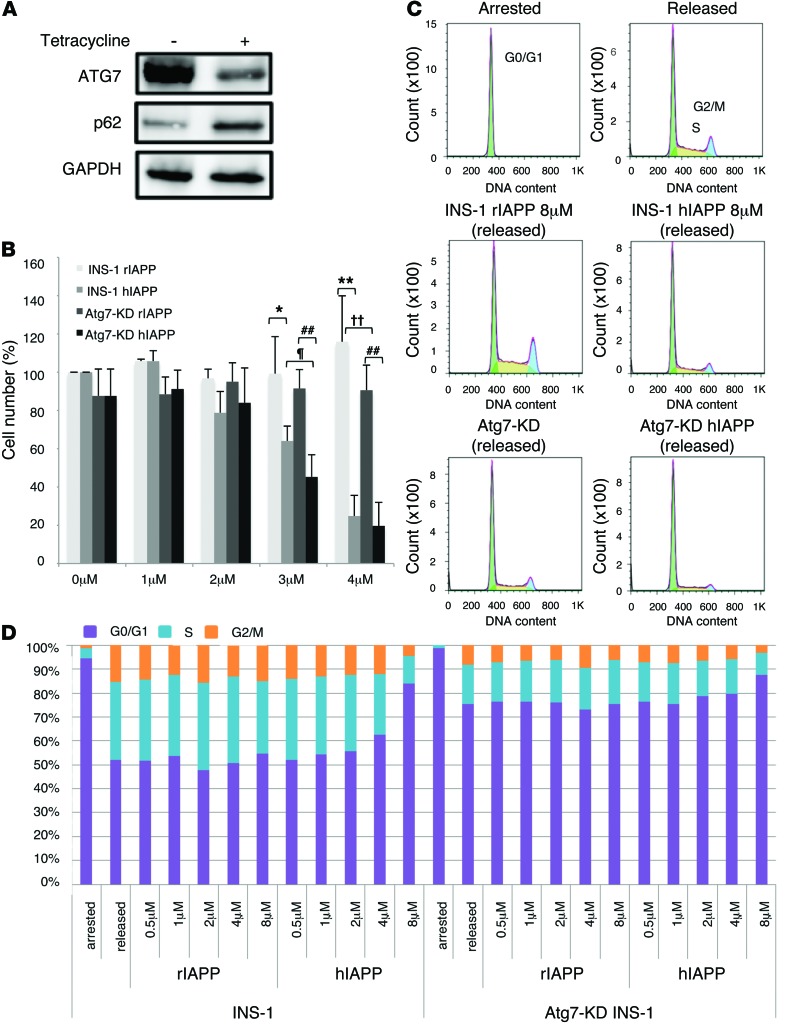
Figure 2. Effects of hIAPP/rIAPP and autophagy deficiency on cell cycle and viability of INS-1 cells.
(A) Association of reduced ATG7 with accumulation of p62 in Atg7-KD INS-1 cells with tetracycline supplementation. GAPDH served as loading control. (B) INS-1 and Atg7-KD INS-1 cells were cultured in the presence of 0–4 μM rIAPP or hIAPP peptide for 48 hours. The number of cells not stained with Trypan Blue was counted; cell number is presented as percentage of control (0 μM IAPP). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, INS-1 rIAPP vs. INS-1 hIAPP; ††P < 0.01, INS-1 rIAPP vs. Atg7-KD rIAPP; ##P < 0.01, Atg7-KD rIAPP vs. Atg7-KD hIAPP; ¶P < 0.05, INS-1 hIAPP vs. Atg7-KD hIAPP. (C and D) FACS histograms (C) and stacked bar graphs (D) of INS-1 cells grown under conditions of growth arrest (induced by exposure to 2.8 mMol/l glucose and serum withdrawal for >24 hours) and after release from arrest (by 22.2 mMol/l glucose, 200 nMol/l insulin, hIAPP/rIAPP, and serum withdrawal medium for 24 hours).