Figure 9.
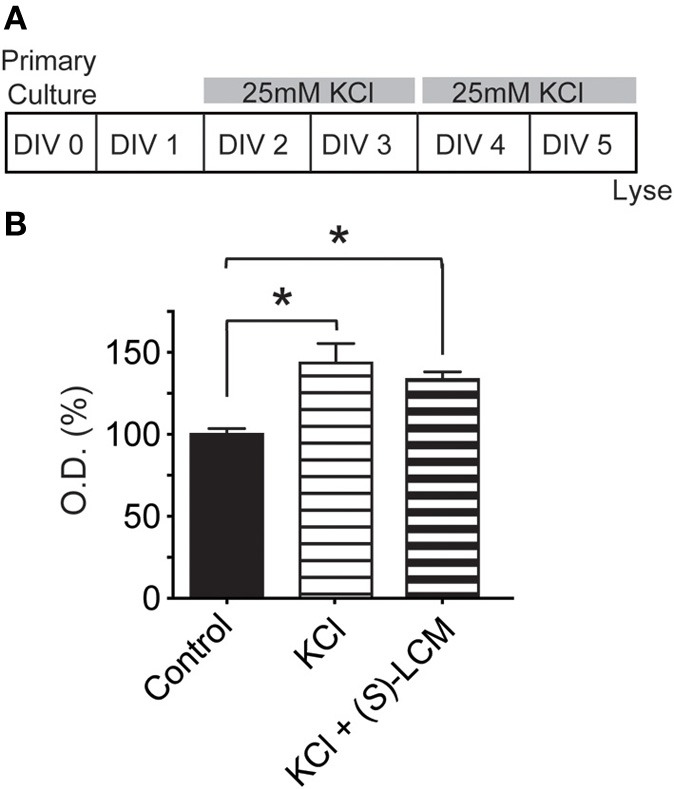
Chronic KCl depolarization increases the association of CRMP2 and tubulin. (A) Timeline of experimental procedures. (B) Summary of CRMP2-binding to tubulin from cortical cell lysates as determined by ELISA. The values obtained from these experiments are arbitrary optical densities. Thus, we have normalized the values of treated groups to the control group, which was set to 100%. This allows us to compare values across experiments. KCl exposure increased CRMP2 binding by ~43.5% compared to control. As (S)-LCM was previously shown not to impact CRMP2/tubulin binding, its co-application did not alter the effect of KCl. (*p < 0.05 compared to control; One-Way ANOVA, Tukey's post-hoc analysis) (n = 4).
