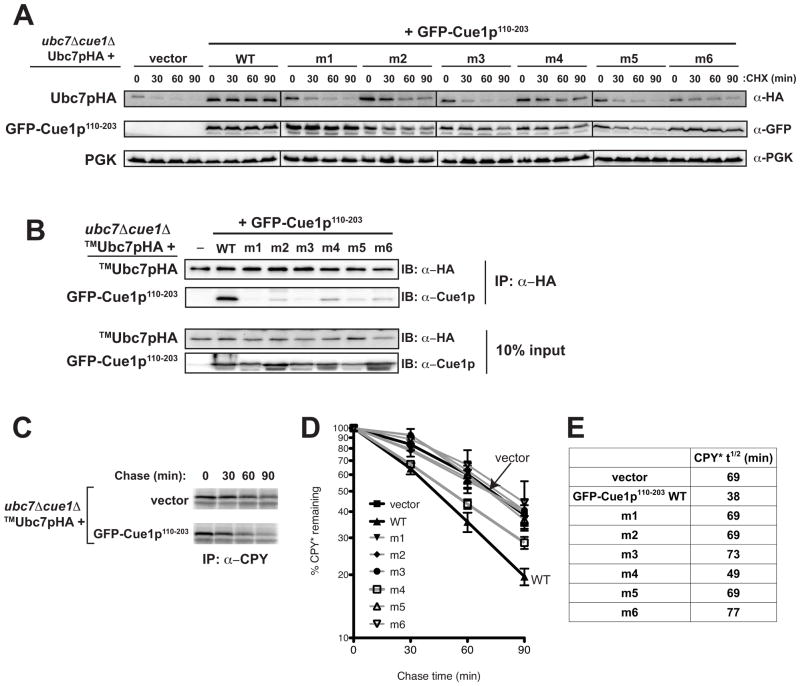
Figure 3.
U7BR contact residues are essential in vivo for Ubc7p’s stability, binding to Cue1p, and ERAD. (A) Degradation of Ubc7pHA and GFP-Cue1p110-203 were assessed by cycloheximide (CHX) chase at the indicated time points using a ubc7Δ cue1Δ strain containing a chromosomal CPY* allele transformed with a low copy plasmid encoding Ubc7pHA and low copy plasmids encoding vector (pRS314) or the indicated GFP-Cue1p110-203 wild-type- or mutant-expressing plasmid. Protein stability was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-GFP antibodies, respectively. PGK was used as a loading control. (B) The binding of transmembrane anchored TMUbc7pHA to the indicated GFP-Cue1p110-203 wild-type or U7BR mutant was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation of TMUbc7pHA from equivalent amounts of detergent-solubilized protein lysates using anti-HA affinity matrix. Bound proteins were eluted, analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and TMUbc7pHA and GFP-Cue1p110-203 wild-type and indicated mutants were visualized by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-Cue1p antibodies, respectively. 10% of each input lysate was also analyzed. (C) The degradation of CPY* was analyzed at the indicated time points by 35S pulse-chase analysis using the indicated strain carrying vector (pRS314) or wild-type GFP-Cue1p110-203. (D) The average of three independent pulse-chase experiments of the GFP-Cue1p110-203 wild-type and mutant strains from (B). Error bars represent the standard error. (E) The half-life (t1/2, in min) of CPY* in each of the strains was calculated from the graphs in (D).