Figure 1.
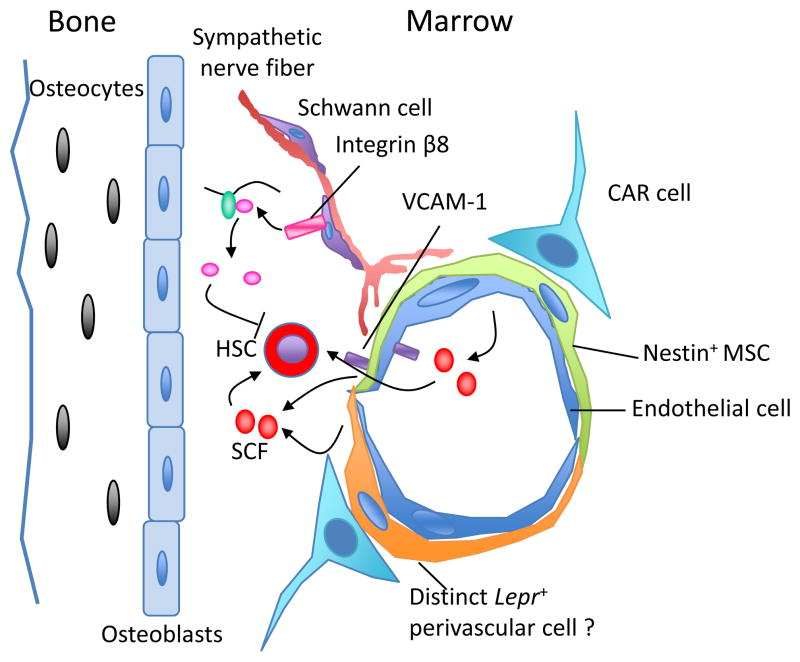
The complex cellular and molecular make up of the HSC niche in the bone marrow. A variety of cells, including osteoblasts, Cxcl12-abundant reticular (CAR) cells, Nestin-positive mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), Lepr-expressing perivascular cells and endothelial cells have been shown as possible components of the niche. Cells from the neural system, nonmyelinating Schwann cells wrapping sympathetic nerve fibers, promote HSC quiescence through activation of TGF-β. The structural composition of these cells provides a specialized microenvironment that regulates HSC self-renewal and differentiation, either though contact-dependent signals such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1)6, or via soluble factors such as SCF.