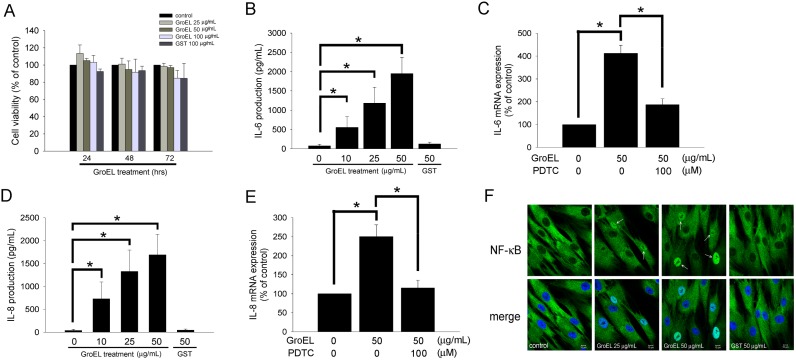
Figure 1. P. gingivalis GroEL induces IL-6 and IL-8 production in PDL cells, potentially via NF-κB activation.
(A) Cellular cytotoxicity of recombinant P. gingivalis GroEL was analyzed by MTT assay. PDL cells were treated with serum-free medium (0 µg/mL; control), 25–100 µg/mL GroEL or 100 µg/mL GST for 24–72 h; an MTT assay was performed, and the absorbance was recorded using a microplate reader. (B and D) PDL cells were treated with serum-free media containing 0–50 µg/mL GroEL or 50 µg/mL GST for 24 h. The levels of IL-6 (B) and IL-8 (D) in the culture media were quantified via ELISA assay, and the absorbance was recorded using a microplate reader. (C and E) PDL cells were treated with serum-free medium (0 µg/mL; control), 50 µg/mL GroEL or 100 µM pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) plus 50 µg/mL GroEL for 12 h. The expression of IL-6 (C) and IL-8 (E) mRNA was analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p<0.05 was considered significant. (F) PDL cells grown on slides were exposed to serum-free medium (0 µg/mL; control), GroEL (25 or 50 µg/mL) or 50 µg/mL GST for 120 min and then imaged on a confocal microscope after immunofluorescence staining against NF-κB p65 was performed. The lower images are merged pictures of the upper images with Hoechst staining for nuclei. White arrows indicate activated NF-κB p65 in the nuclei. The scale bar indicates 10 µm.