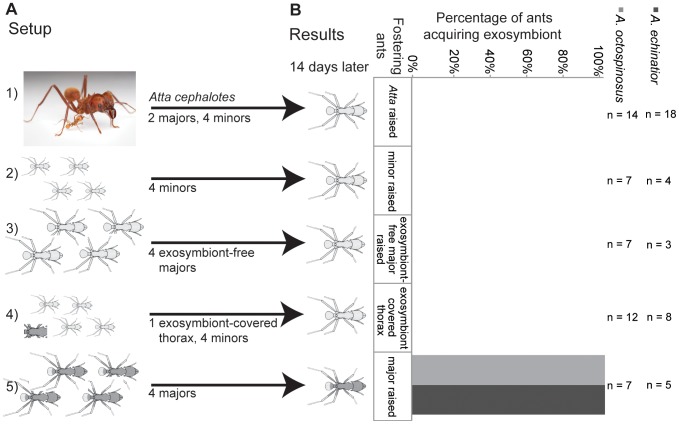
Figure 1. Acquisition source.
a) Subcolony set-up. Newly eclosing Acromyrmex workers were fostered in subcolonies containing the following components 1) Atta cephalotes ants, a genus lacking visible symbiont, 2) minor workers (also lacking visible symbiont), 3) major workers without visible symbiont, 4) dissected thorax from major workers (changed every 48 hours) and minor workers (lacking visible symbiont) and 5) major workers with visible symbiont. Only pupae fostered with living major workers carrying Pseudonocardia developed symbiont coverage. b) The results of this experiment showed that Acromyrmex echinatior and Ac. octospinosus successfully acquired exosymbiotic bacteria only when pupae were raised in the presence of major workers carrying exosymbiont. Sample sizes (n) represent the number of focal ants surviving more than five days after eclosion. See Figure S1 for mortality data. Photo of Atta cephalotes used with permission, ©Alex Wild, Schematic ant drawings modified from Poulsen et al. [18].