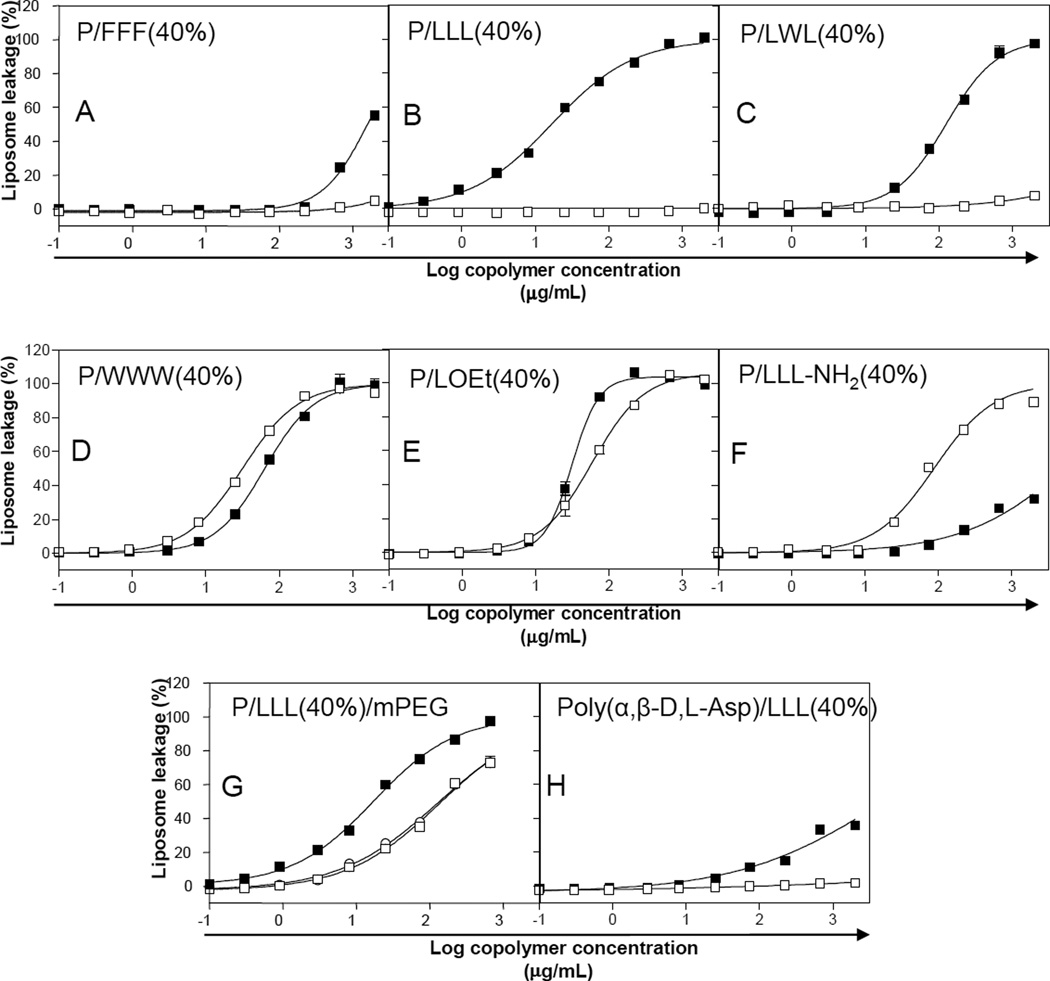
Fig. 2.
Membranolytic activity of various copolymers. Liposome leakage was measured as a function of concentration at pH 7.4 (□) and 5.0 (▪) using the standard liposome leakage assay. Copolymers of PMLA and triphenylalanine (P/FFF) (A), trileucine (P/LLL) (B), and leucyltryptophanylleucine (P/LWL) (C) showed membranolytic activity only at pH 5.0. Copolymers of PMLA and tritryptophan (P/WWW) (D),leucine ethyl ester (P/LOEt) (E) and trileucine amide (PLLLNH2) (F) showed membranolytic activity at both pH 5.0 and 7.4. Copolymers P/LLL(40%) (-▪-) containing mPEG5000 (−○−, 3%) and mPEG5000 (-□-, 5%) (G) showed reduced membranolytic activity at pH 5.0 when mPEG5000 was an additional substituent. Copolymer consisting of poly(α,β-d,l-Asp) and trileucine (H) showed pH- dependent membranolytic activity. Curves in all figures were obtained by fitting with sigmoidal dose-response curves according to GraphPad Prism 3.02. Data are the means ±SEM in triplicate.