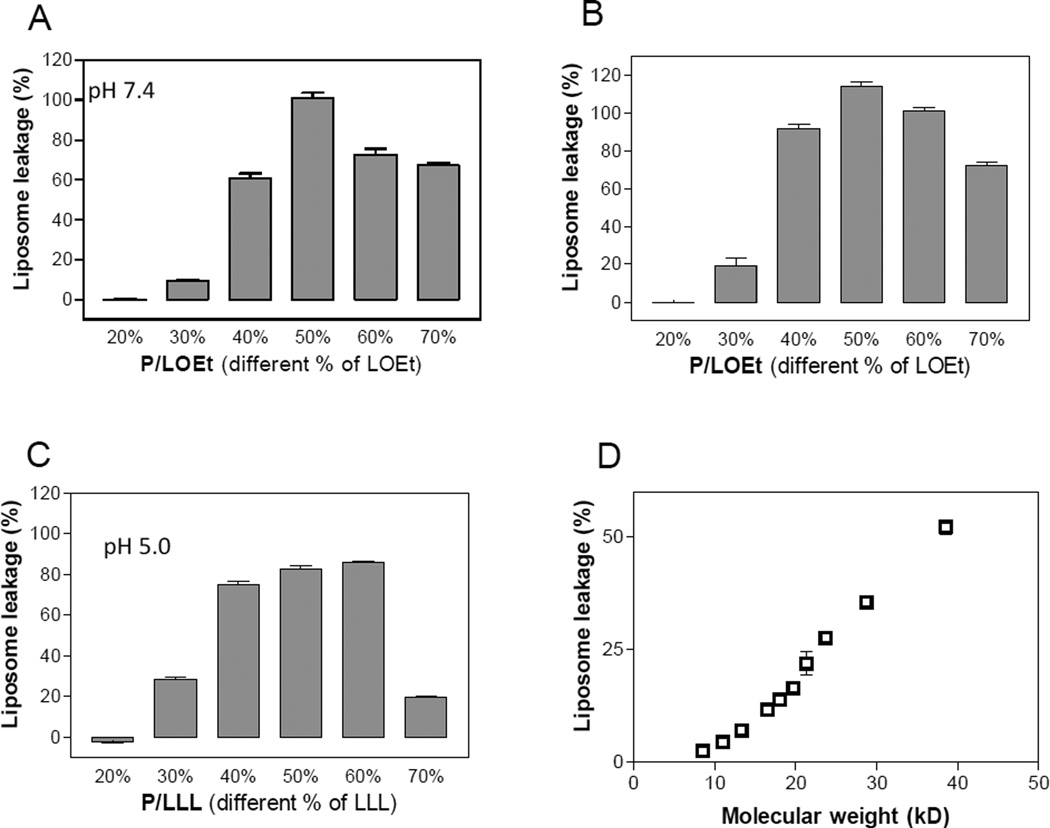
Fig. 4.
Effects of substituent loading density (%) and molecular weight of the polymer platform. Membranolytic activities were measured using the standard liposome leakage assay. A – C, copolymers P/LLL and P/LOEt with varying amounts of loaded LLL (pH 5.0) or LOEt (pH 5.0 and pH 7.4) at a constant concentration of polymer platform 75 µg/mL. Optimal liposome leakage is seen for ∼ 50% substitution of carboxyl groups. D, membranolyticacitivity of copolymer P/LLL(50%) as a function of varied molecular weight at the copolymer concentration of 0.25 µM. Data represent means ± SEM in triplicate.