Figure 7.
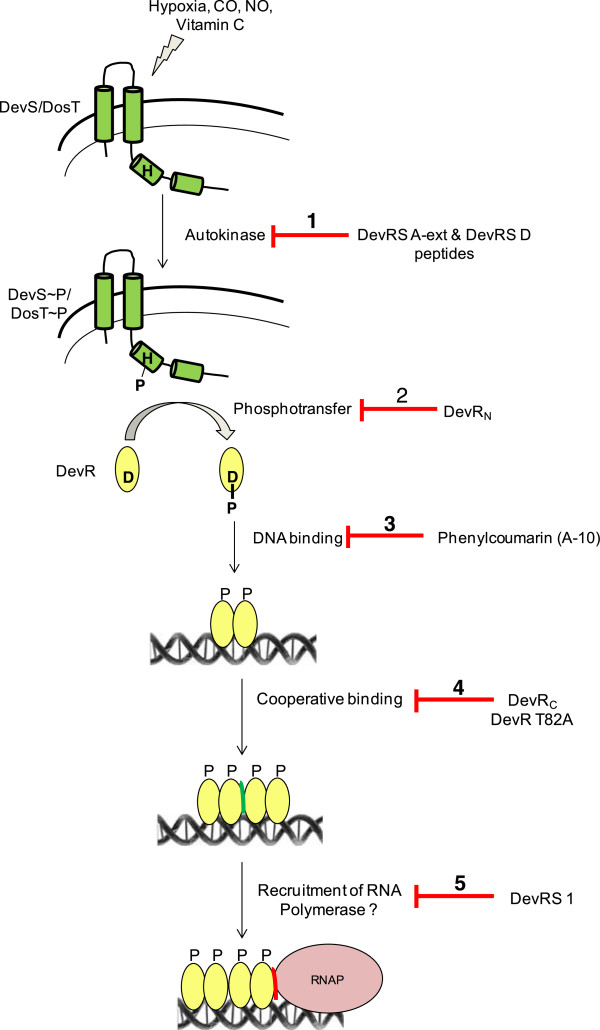
Interception of the DevRS signaling cascade. Hypoxia, NO, CO, and Vitamin C are sensed by DevS and DosT kinases (represented as membrane-associated sensors), resulting in the transfer of the phosphosignal from the sensors to DevR leading to its activation. Phosphorylated DevR binds to target gene promoters and elicits regulon activation. The red line/bars indicate the various steps in this signalling cascade whose interception results in a defect in the hypoxic adaptation of M. tb. Step 1, the inhibition of DevS/DosT autokinase activity by DevRS A-ext and DevRS D peptides (this study) interrupts the initial step in two-component signalling. Step 2, DevRN protein competes with full-length DevR protein at the phosphotransfer step to inhibit bacterial adaptation [21]. Step 3, phenylcoumarin A-10 functions by inhibiting the binding of DevR to DNA [20]. Step 4, the cooperative interaction of DevR with DNA (green interface between 2 dimers of DevR) is required for robust induction [16,25], and serves as a novel inhibition step. Step 5, a DevR interacting peptide DevRS1 [15] likely exerts its inhibitory effect by blocking the between DevR - RNA polymerase interaction (red interface).
