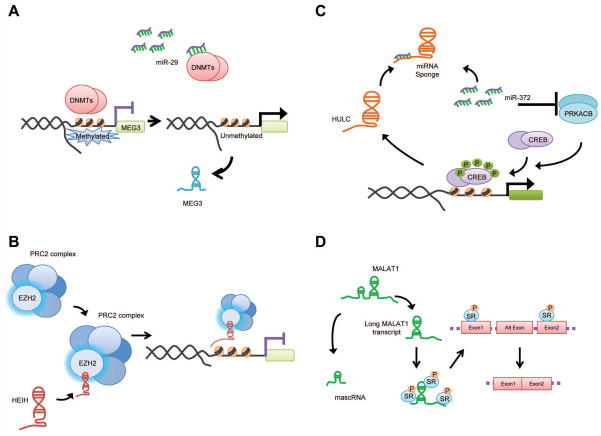
Figure 6. Mechanisms of action of selected lncRNA.
lncRNA can be regulated or act through a variety of mechanisms that involve diverse processes such as transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of gene expression, regulation of splicing and interactions with miRNA. Mechanisms that have been described for MEG3, HEIH, HULC and MALAT-1 are depicted to illustrate the diversity of interactions between lncRNA and other proteins and RNA molecules. (A) miRNA dependent regulation of lncRNA expression. Methylation at the MEG3 promoter is regulated by DNMTs. Modulation of DNMTs by miR-29 contributes to regulation of MEG3 expression. (B) Epigenetic regulation. HEIH associates with the EZH2 subunit of the PRC2 complex, and recruits this complex to a specific gene locus and contributes to the expression of EZH2-regulated target genes. (C) Targeting miRNA. HULC acts as a molecular sponge to sequester miR-372 and reduce the repression of its target gene PRKACB thereby enabling phosphorylation and activation of the CREB transcription factor, which in turn stimulates HULC expression. (D) Regulation of alternative splicing. The full length of MALAT-1 transcript is processed to generate two non-coding RNAs. The larger MALAT-1 RNA transcript is retained in the nuclear speckles and can modulate the activity of serine/arginine (SR) splicing factors to potentially regulate alternative splicing.