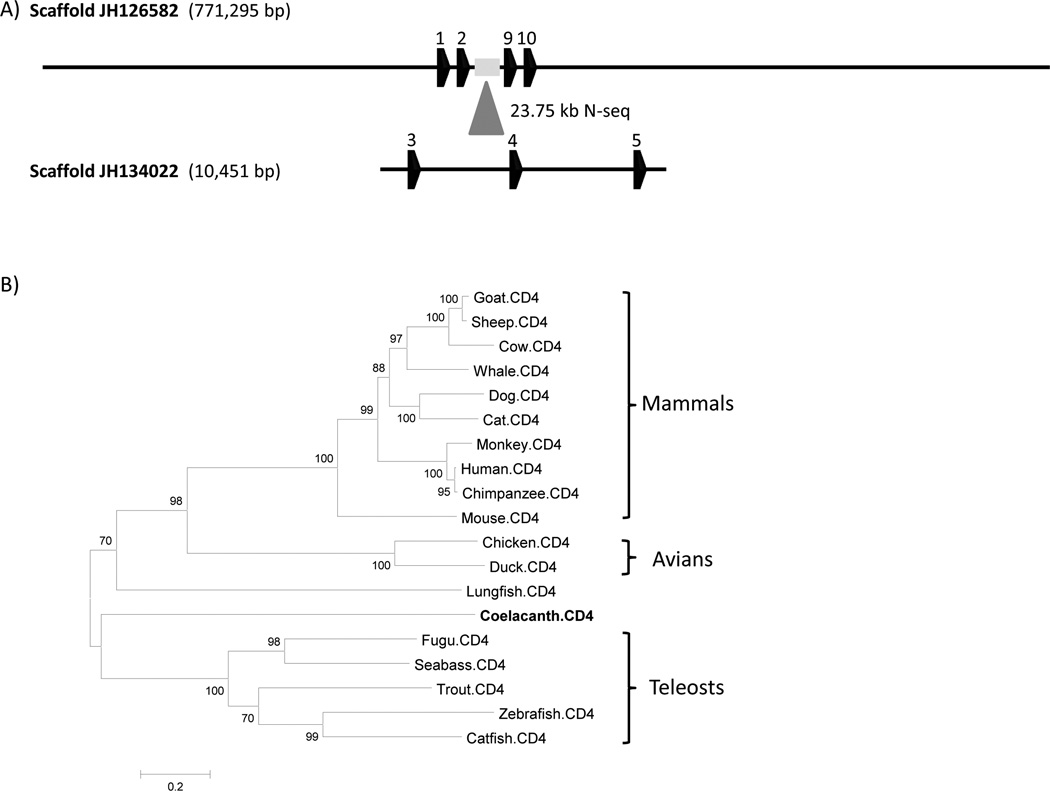
Figure 11. Coelacanth CD4 annotation and phylogenetic analysis.
(A) Two scaffolds, JH126582 and JH10451, contain 4 and 3 exons, respectively. Scaffold JH134022, which contains exon 3, 4 and 5, maps to the assembly gap (∼ 23.75 kb) of scaffold JH126582. (B) The unrooted phylogenetic tree was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. The analysis involved 19 CD4 amino acid sequences, with a total of 535 positions in the final dataset. The resolution of the coelacanth and lungfish branches is poor due to the deep branch lengths. GenBank accession numbers of CD4s: Zebrafish (NP_001128568), fugu (NP_001072091), trout (NP_001118011), catfish (ABD93355), seabass (CAO98731), chicken (NP_989980), duck (AF378701), chimpanzee (NP_001009043), human (NP_000607), mouse (NP_038516), dog (NP_001003252), cow (NP_001096695), cat (NP_001009250), monkey (CAA51752), sheep (NP_001123374), whale (NP_001267583), goat (ACG76115).