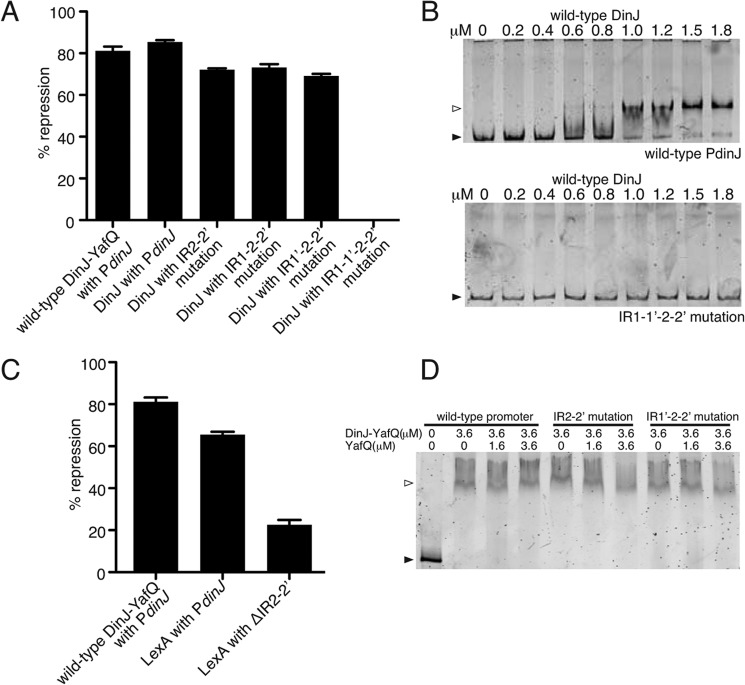
FIGURE 6.
Transcriptional repression and direct binding of DinJ and LexA at the dinJ promoter. A, β-galactosidase assays using the same dinJ operator mutations as in Fig. 5B, but instead testing repression by DinJ alone. Mutation of all four IRs (IR1–1′ to 2–2′) resulted in a complete loss of transcriptional repression by DinJ and thus is depicted as 0% repression. B, EMSAs of increasing concentrations of wild-type DinJ binding to either wild-type or IR1–1′ to 2–2′ mutated dinJ promoter region, respectively. C, β-galactosidase assays testing repression by LexA. D, complexes of wild-type DinJ-YafQ-dinJ promoter were incubated with an increasing molar excess of YafQ as indicated. Black-filled arrows and open arrows indicate unbound and TA-bound DNA, respectively. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. of reactions performed in triplicate for assays in A and C.