FIGURE 3.
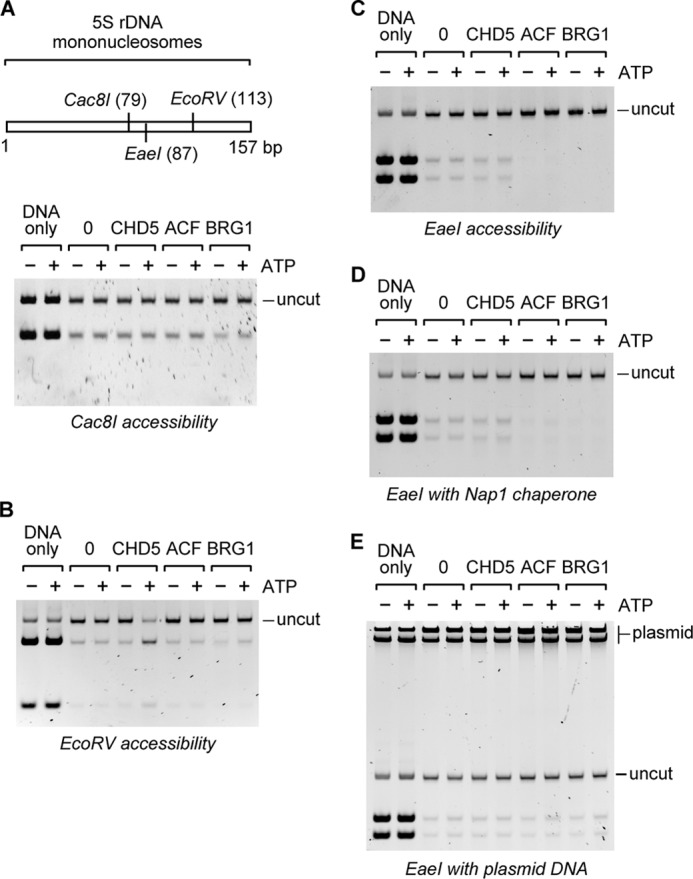
CHD5 increases accessibility of mononucleosomal DNA at specific sites. Mononucleosomes lacking extranucleosomal DNA were reconstituted on a natural 5 S rDNA positioning sequence and incubated with CHD5 in the presence of a restriction enzyme. A, schematic of the mononucleosome DNA with restriction sites and their positions indicated in parentheses. Mononucleosomes were incubated with CHD5 and digested with Cac8I, which cleaves at the dyad, or (B) with EcoRV, which cleaves at a single site at ∼44 bp from one end, or (C) with EaeI, which cleaves at a single site ∼70 bp from one end. To aid in the capture of potentially released histones, the histone chaperone NAP1 (D) or plasmid DNA (indicated as plasmid at the top of the gel) (E) was included in the EaeI digestion reactions. DNA corresponding to full-length mononucleosomal DNA is indicated as uncut. Samples incubated in the absence of remodeling factors are indicated by 0. DNA-only refers to samples with naked DNA.
