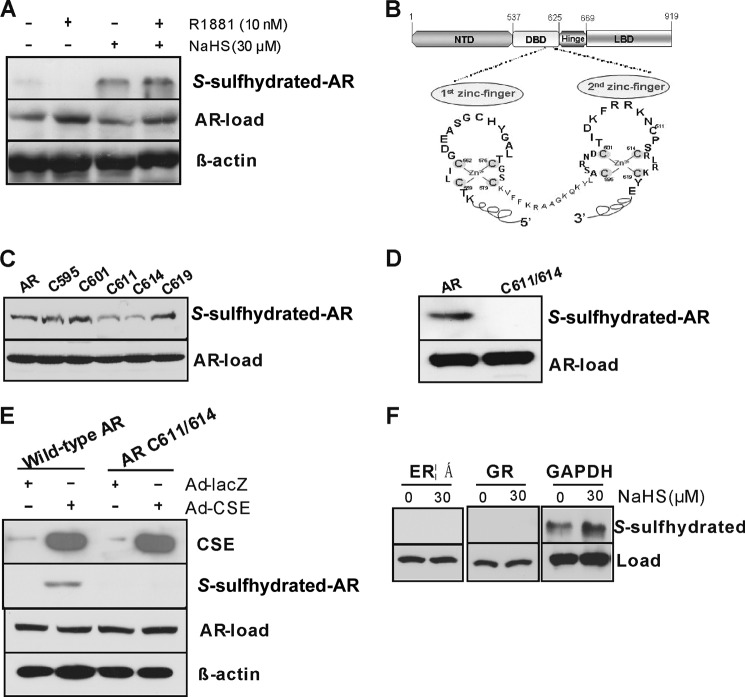
FIGURE 6.
H2S S-sulfhydrates AR at the second cysteine-rich zinc finger module. A, H2S S-sulfhydrated AR in LNCaP cells. The cells were incubated with R1881 (10 nm) with or without NaHS (30 μm) for 48 h. AR-load, samples were run on blots alongside total lysates and subjected to immunoblotting with antibody specific to AR. B, the structure domain of AR gene and its two cysteine 4-type zinc fingers in AR-DBD. C, single mutation of cysteine 611 (C611) or cysteine 614 (C614) but not other cysteine resides diminished H2S S-sulfhydration of AR. NTD, N-terminal domain; LBD, ligand-binding domain. D, double mutations of cysteine 611/614 completely eliminated H2S S-sulfhydration of AR. Cos-1 cells were transfected with the mutants for 48 h in the presence of NaHS (30 μm). E, CSE overexpression induced AR S-sulfhydration. Cos-l cells were transfected with Ad-LacZ or Ad-CSE with or without wild-type AR or AR cysteine 611/614 mutant for 48 h. F, H2S had no effect on GR and ERα S-sulfhydration. LNCaP cells were incubated NaHS (30 μm) for 48 h. GAPDH acted as a positive control. AR S-sulfhydration was detected by biotin switch assay with anti-AR antibody (A), anti-GFP antibody (C, D, and E), or anti-ERα and GR (F). The experiments were repeated at least three times.