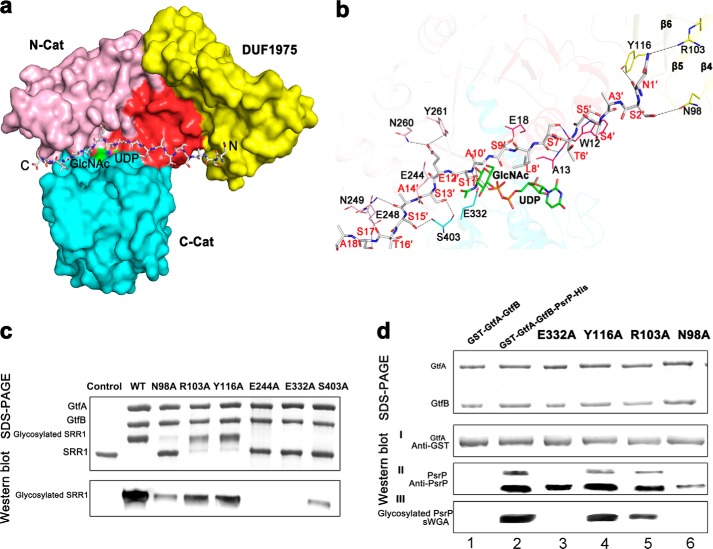
FIGURE 4.
A docking model of the N-terminal octadecapeptide of SRR1 binding to GtfA. a, surface presentation of the acceptor peptide-binding site. The four segments of GtfA are colored red, yellow, pink, and cyan, respectively. The octadecapeptide is shown in gray sticks with the N and C termini labeled. The UDP and GlcNAc molecules are colored green. b, a close-up view of the interactions of the octadecapeptide with GtfA. The structure of GtfA was shown as semi-transparent cartoon. The interacting residues and the octadecapeptide are shown as sticks. The polar interactions are indicated as dashed lines. c, in vitro O-GlcNAcylation assays of GtfA and its mutants in the presence of GtfB and GST fused SRR1. The reaction mixtures were separated by electrophoresis and further subjected to Western blot analysis using WGA-HRP conjugate. d, DUF1975 is important for binding of GtfA to the acceptor PsrP. An E. coli recombinant system that co-expresses GtfA or GtfA variants with its acceptor PsrP was used to determine binding of GtfA to PsrP and the function of DUF1975 in the binding. Purified GST fused GtfA and GtfA variants (I),and its interacting partners PsrP (II) were determined by Western blot analysis using anti-GST antibody and anti-PsrP antibody and by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. Proteins prepared from GtfA-GtfB alone and co-expression of wild-type GtfA and variants (E322A, Y116A, R106A, and N98A)-GtfB with PsrP were also subjected to wheat germ agglutinin lectin blotting analysis (III).