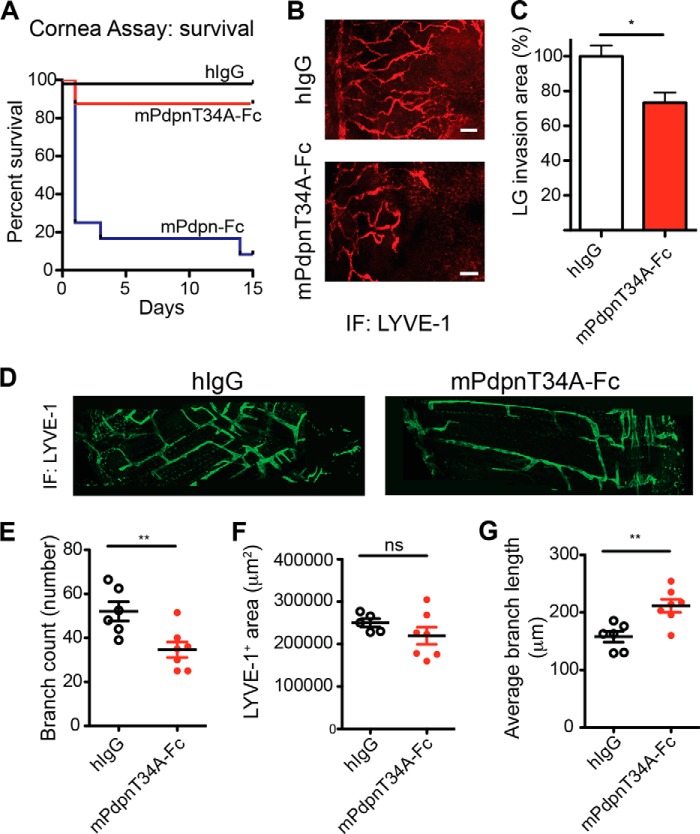
FIGURE 5.
mPdpnT34A-Fc retains full ability to inhibit lymphangiogenesis in vivo. A, three sutures were placed on the corneas of BALB/c mice and 70 μg of mPdpn-Fc (n = 12), mPdpnT34A-Fc (n = 8), or IgG control (n = 8) were injected into the subconjunctival space twice weekly for 2 weeks. Survival of the animals in the different treatment groups is shown by a Kaplan-Mayer curve. Although animals injected with mPdpnT34A-Fc or hIgG survived, 80% of animals treated with mPdpn-Fc died after the first or second injection. B and C, lymphatic vessel invasion into the cornea was quantified by staining for the lymphatic-specific marker LYVE-1 and was found to be significantly lower in mPdpnT34A-Fc-treated animals compared with human IgG control. D, diaphragms of 5-day-old mice treated in utero at E16.5 and 18.5 wher stained for LYVE-1. mPdpnT34A-Fc-treated mice had a less complex diaphragmatic lymphatic network. E–G, confocal images of diaphragmatic branches were morphometrically analyzed for the parameters branch number, LYVE-1-stained area, and average branch length. The mPdpnT34A-Fc-treated mice had a less complex lymphatic network characterized by less but longer branches. Data represent mean ± S.E., statistical significance was analyzed using the unpaired Student's t test, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.