FIGURE 9.
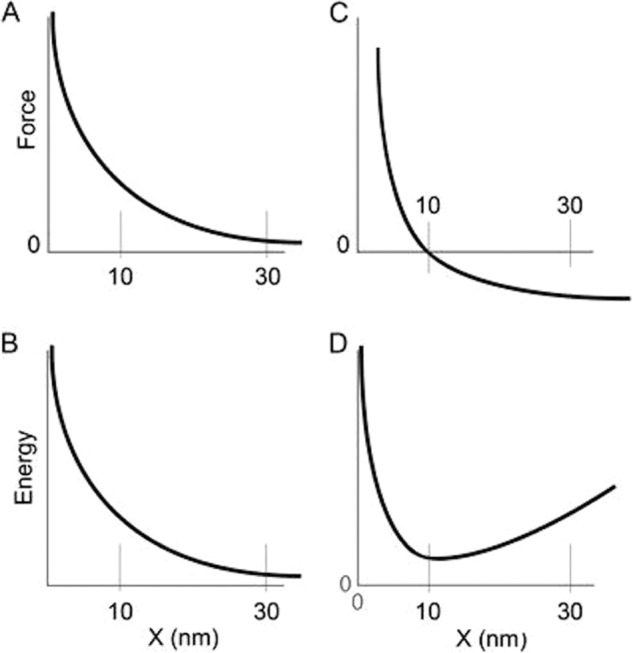
Comparison of two models or mechanisms by which an S2 domain might enhance shortening speeds. A and B, force-distance plot (A) and energy-distance plot (B) if the S2 domain moves from a high force to a low force state over a distance x. Note that the apparent step size is larger than that because of the heads alone (10 nm) because of the involvement of the S2 (30 nm). C and D are the corresponding plots if S2 decreases forces that resist shortening through a mechanism similar to that proposed by Kaya and Higuchi (56). The driving force is exerted over a distance equal to the 10-nm myosin step size, and movement beyond this point results in minimal resistive (negative) forces.
