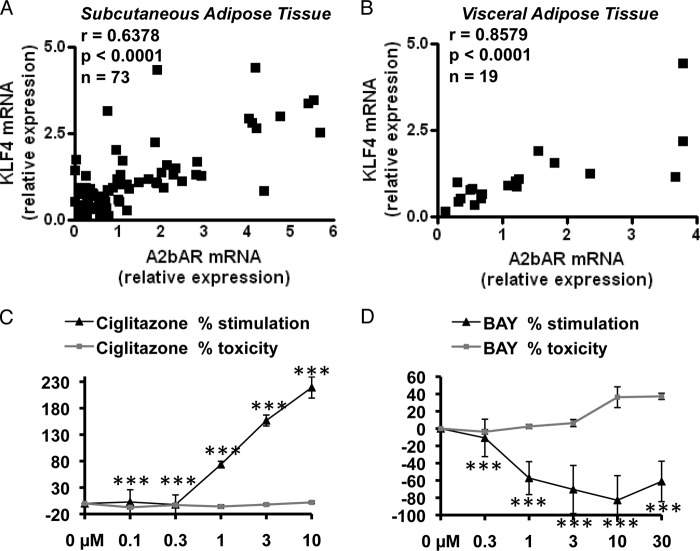
FIGURE 8.
KLF4 and A2bAR are correlated significantly in human adipose tissue. Subcutaneous (A, n = 73) and visceral (B, n = 19) adipose tissues were obtained from obese individuals. As described under “Experimental Procedures,” mRNA was extracted from the samples, and mRNA expression was determined by using the ΔΔCT method and normalized to 18 S rRNA values. Spearman correlation coefficients (r) were calculated comparing mRNA expression of A2bAR to KLF4. C and D, human preadipocytes were isolated and differentiated to adipocytes for 10 days as described previously (24, 25). During differentiation, cells were treated with increasing concentrations (0, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, and 10 μm) of ciglitazone, a thiazolidinedione and potent and selective PPARγ ligand (C), BAY 60-6583 (BAY) (D), or vehicle control (DMSO) every other day during induction. On day 10, adipocytes were stained with BODIPY fluorescent fatty acid (which becomes incorporated into lipid filled cells), and relative fluorescence compared with vehicle treatment was measured using a Tecan microplate reader. Cell viability was determined by CellTiter-Blue assay. The percent stimulation of adipogenesis (measured by adipocyte staining) and toxicity over control treatment was determined for each concentration (n = 3). Data are mean ± S.E. ***, p < 0.001 compared with vehicle treatment at the same concentration. Analyses were performed by Spearman correlation coefficient (A and B) or by Student's t test (C and D).