Figure 1.
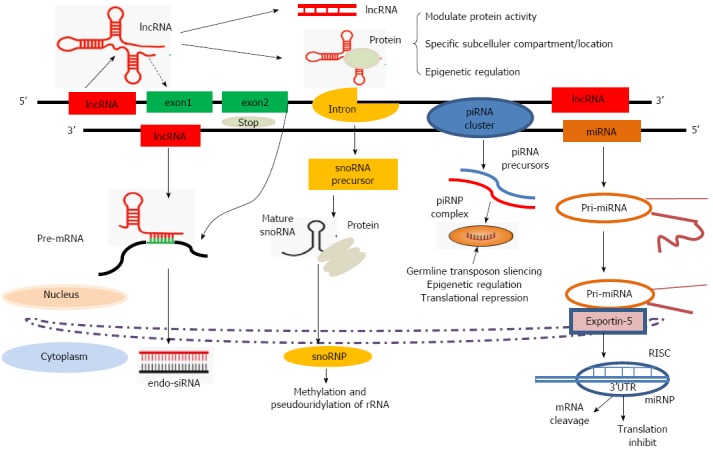
Biogenesis and functional machinery of small ncRNAs (miRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs) and lncRNAs. (1) miRNAs: pri-miRNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase II, then cleaved by Droshain into pre-miRNA. Pre-miRNAs are then transported to the cytoplasm via an Exportin-5-mediated mechanism and further processed by the RNase III endonuclease into mature miRNAs. Mature miRNAs are then incorporated into the RISC, where they direct the complex to specific mRNAs through complementary base pairing in their 3’UTRs; (2) piRNAs: piRNAs are mainly expressed from piRNA clusters. Subsequently, additional piRNAs influence the functions of ribonucleoprotein (piRNP) complexes in transposon repression through target degradation and epigenetic silencing; (3) snoRNAs: snoRNAs are transcribed from introns. Following splicing, debranching and trimming, mature snoRNAs are either exported, in which case they function in rRNA processing, or remain in the nucleus, where they are involved in alternative splicing; and (4) lncRNAs: lncRNAs exhibit a 5’ terminal methylguanosine cap and are often spliced and polyadenylated. lncRNAs contain structural domains that can sense or bind to other RNAs via complementary base pair interactions, in addition to interacting with proteins and possibly DNA and displaying other as yet unknown functions. endo-siRNA: Endogenous small-interfering RNA; lncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; miRNA, microRNA; piRNA: PIWI-interacting RNA; pre-miRNA: Primary miRNA; pre-miRNA: Precursor miRNA; rRNA: Ribosomal RNA; RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex; sncRNA: Small non-coding RNA; snoRNA: Small nucleolar RNA; 3’UTRs: 3’ untranslated regions.
