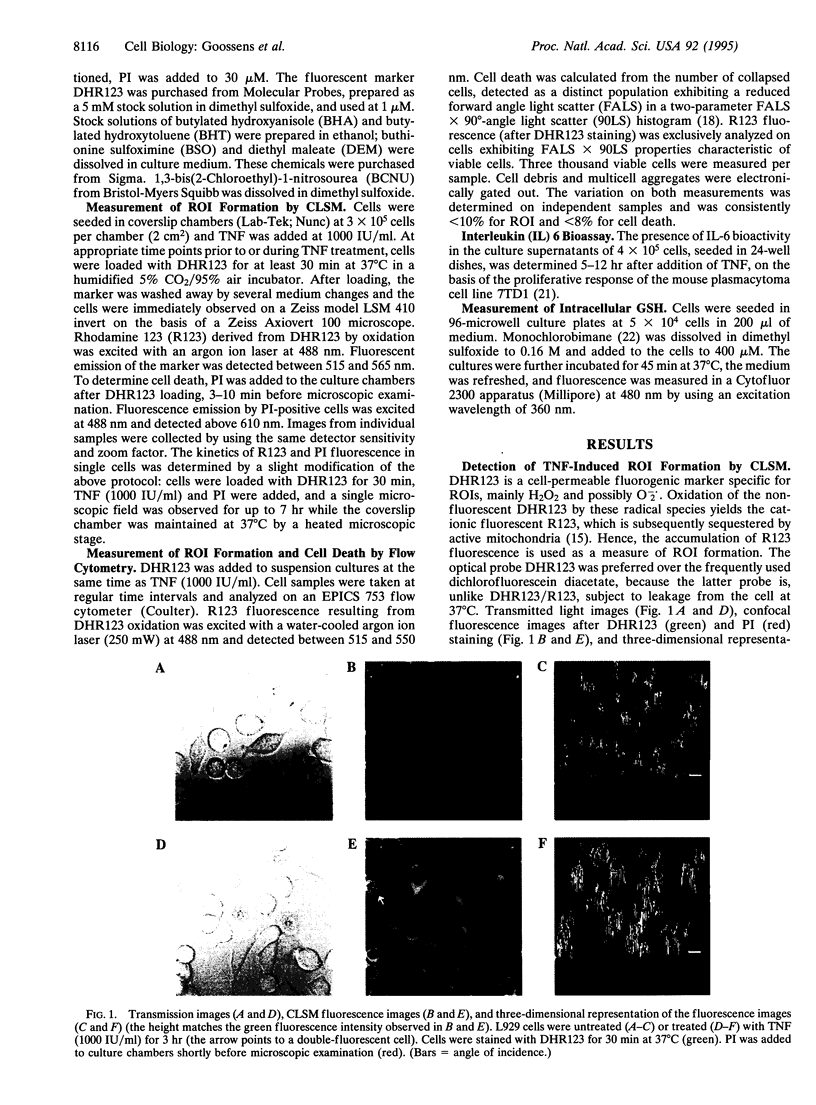
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is selectively cytotoxic to some types of tumor cells in vitro and exerts antitumor activity in vivo. Reactive oxygen intermediates (ROIs) have been implicated in the direct cytotoxic activity of TNF. By using confocal microscopy, flow cytometry, and the ROI-specific probe dihydrorhodamine 123, we directly demonstrate that intracellular ROIs are formed after TNF stimulation. These ROIs are observed exclusively under conditions where cells are sensitive to the cytotoxic activity of TNF, suggesting a direct link between both phenomena. ROI scavengers, such as butylated hydroxyanisole, effectively blocked the formation of free radicals and arrested the cytotoxic response, confirming that the observed ROIs are cytocidal. The mitochondrial glutathione system scavenges the major part of the produced ROIs, an activity that could be blocked by diethyl maleate; under these conditions, TNF-induced ROIs detectable by dihydrorhodamine 123 oxidation were 5- to 20-fold higher.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyaert R., Fiers W. Molecular mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity. What we do understand and what we do not. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 28;340(1-2):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casini A. F., Pompella A., Comporti M. Liver glutathione depletion induced by bromobenzene, iodobenzene, and diethylmaleate poisoning and its relation to lipid peroxidation and necrosis. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):225–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmendörffer A., Hecht M., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Roesler J. A fast and easy method to determine the production of reactive oxygen intermediates by human and murine phagocytes using dihydrorhodamine 123. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Aug 7;131(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Müller R., Marmenout A., Tavernier J., Van der Heyden J., Kawashima E., Chollet A., Tizard R., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Vliet A. Molecular cloning of mouse tumour necrosis factor cDNA and its eukaryotic expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4417–4429. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Origin and turnover of mitochondrial glutathione. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4668–4672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Origin and turnover of mitochondrial glutathione. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4668–4672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grooten J., Goossens V., Vanhaesebroeck B., Fiers W. Cell membrane permeabilization and cellular collapse, followed by loss of dehydrogenase activity: early events in tumour necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity. Cytokine. 1993 Nov;5(6):546–555. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4666(05)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Neale M. L., Jackson S. K., Stark J. M. Tumour cell killing by tumour necrosis factor: inhibition by anaerobic conditions, free-radical scavengers and inhibitors of arachidonate metabolism. Immunology. 1987 Sep;62(1):153–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Gifford G. E. Stimulation of RNA synthesis in L-929 cells by rabbit tumor necrosis factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Mar;160(3):354–358. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed D. J. Glutathione: toxicological implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:603–631. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter C. Pro-oxidants and mitochondrial Ca2+: their relationship to apoptosis and oncogenesis. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 28;325(1-2):104–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81423-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe G., Emmendörffer A., Oser A., Roesler J., Valet G. Flow cytometric measurement of the respiratory burst activity of phagocytes using dihydrorhodamine 123. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Apr 8;138(1):133–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90074-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Newman C., Williamson D. H. A simple cytochemical technique for demonstration of DNA in cells infected with mycoplasmas and viruses. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):461–462. doi: 10.1038/253461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Bakker A. C., Vanhaesebroeck B., Beyaert R., Jacob W. A., Fiers W. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor is mediated by early damage of mitochondrial functions. Evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial radical generation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5317–5323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Beyaert R., Vandevoorde V., Haegeman G., Fiers W. Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3095–3104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrieve D. C., Bump E. A., Rice G. C. Heterogeneity of cellular glutathione among cells derived from a murine fibrosarcoma or a human renal cell carcinoma detected by flow cytometric analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14107–14114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffys P., Beyaert R., Van Roy F., Fiers W. Reduced tumour necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity by inhibitors of the arachidonic acid metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):735–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanke H. J., van der Linden P. W., Langerak J. Alternative fluorochromes to ethidium bromide for automated read out of cytotoxicity tests. J Immunol Methods. 1982;52(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lint J., Agostinis P., Vandevoorde V., Haegeman G., Fiers W., Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates multiple serine/threonine protein kinases in Swiss 3T3 and L929 cells. Implication of casein kinase-2 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases in the tumor necrosis factor signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25916–25921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaesebroeck B., Van Bladel S., Lenaerts A., Suffys P., Beyaert R., Lucas R., Van Roy F., Fiers W. Two discrete types of tumor necrosis factor-resistant cells derived from the same cell line. Cancer Res. 1991 May 1;51(9):2469–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vietor I., Schwenger P., Li W., Schlessinger J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation and increased tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18994–18999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegmann K., Schütze S., Machleidt T., Witte D., Krönke M. Functional dichotomy of neutral and acidic sphingomyelinases in tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1005–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Induction of manganous superoxide dismutase by tumor necrosis factor: possible protective mechanism. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):941–944. doi: 10.1126/science.3263703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. J., Chan A., Leadon S. A. Oxidative damage in murine tumor cells treated in vitro by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 1;49(7):1644–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]