Figure 1. Results pertaining to genetic architecture.
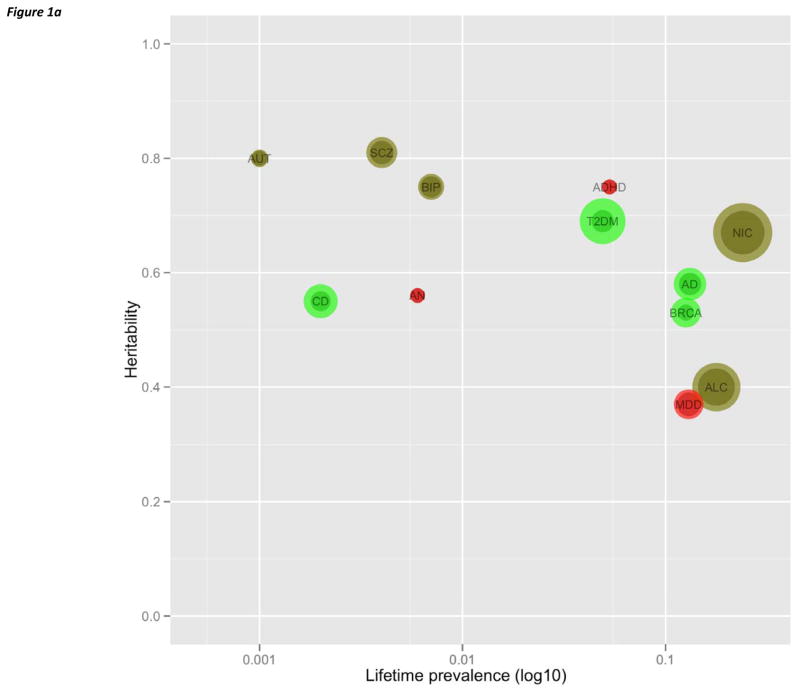
(a) Plot of heritability by log10 lifetime prevalence for nine psychiatric disorders considered in this review plus three complex diseases for which genetic dissection has been particularly successful (Tables 1 and S1). Each disorder is plotted by as heritability by lifetime prevalence. Color indicates qualitative success in identifying etiological genetic variation (green=notably successful, khaki=some successes, red=minimal or no clear success to date). The bubble sizes are proportional to the numbers of cases studied in GWAS (the smaller circle indicating discovery Ncase and the larger circle the total Ncase for discovery plus replication samples). Abbreviations: ADHD=attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, ALC=alcohol dependence, AD=Alzheimer’s disease, AN=anorexia nervosa, ASD=autism, BIP=bipolar disorder, BRCA=breast cancer, CD=Crohn’s disease, MDD=major depressive disorder, NIC=nicotine usage (maximum cigarettes per day), SCZ=schizophrenia, and T2DM=type 2 diabetes mellitus.
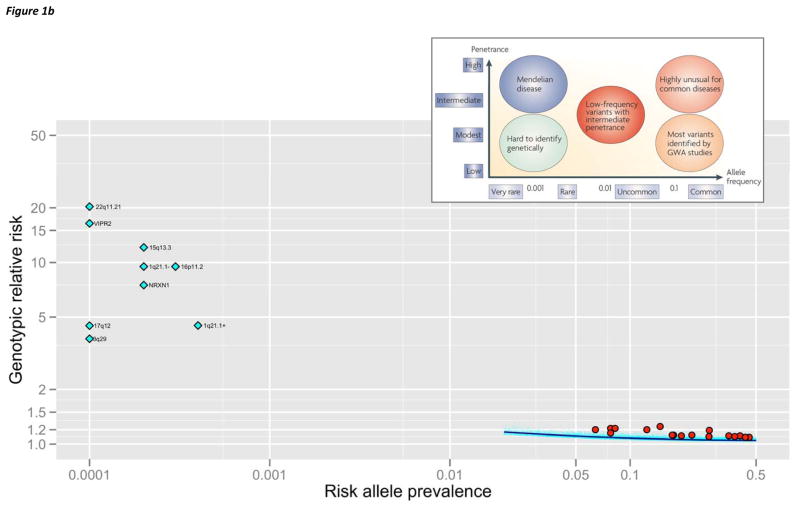
(b) Allelic spectrum of SCZ. The inset is a conceptual schematic from a 2008 Nature Genetics review. 10 The lower part of the figure depicts empirical results for SCZ. The x-axis is log10(AF) in controls. The y-axis is the point estimate for genotypic relative risk (GRR, log10). For clarity, confidence intervals are not shown. There are no known Mendelian variants for SCZ (AF ≪ 0.0001, GRR ≫ 50). There are no known common variants (AF > 0.05) with GRR > 1.5, and these can be excluded with > 99% statistical power. Nine SVs associated with SCZ are shown as light blue diamonds (Table 2, 1q21.1- is the deletion and 1q21.1+ is the duplication). If AF in controls was 0, AF was set to 0.0001. These SVs do not have a corresponding region in the inset. Seventeen common variants have been associated with SCZ (red circles, Table 3). SNPs contributing to the PGC SCZ risk profile score 58 (21,171 autosomal SNPs with PT < 0.1, Box 3, panel b) are shown in light blue dots with a lowess smoother in dark blue.