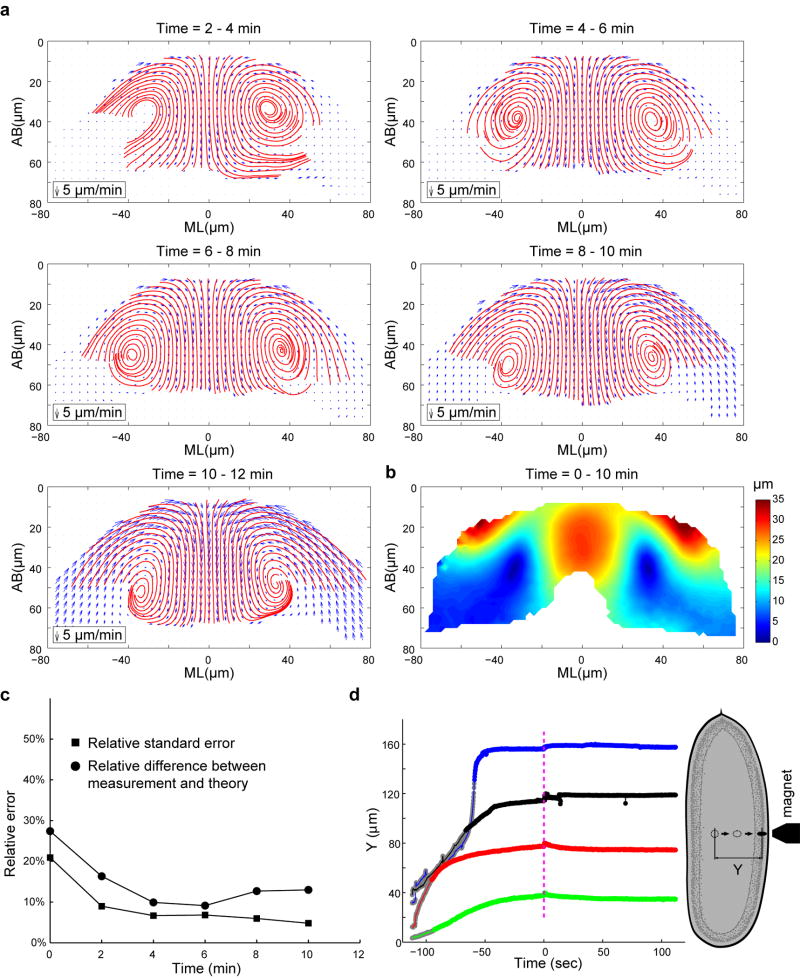
Extended Data Figure 4. Cytoplasmic flow in the wild type embryos at different t.
(a) Velocity field (blue arrows) and streamlines (red) of the cytoplasmic flow in the wild type embryos at different time points during VF formation. The shortening phase starts approximately at t = 10–12 min. (b) Heat map showing the displacement field between t = 0–10 min. (c) Relative difference between the measured velocity profiles in the wild type embryos and the hydrodynamic predictions. Relative standard errors (RSE) of the velocity profiles are plotted for comparison. Note that the relative difference between measurements and predictions is within 13% between t = 4 – 12 min. (d) Displacement of ferrofluid droplets passed through yolk and cytoplasm of syncytial embryos (denoted by Y in the schematic to the right) plotted against time. Blue curve corresponds to a cellularizing wild type embryo; other curves are measurements in double mutant acellular embryos. Magenta dashed line indicates the time-point when magnetic field was removed (t = 0). Y values are normalized such that 40 μm, 80 μm, 120 μm and 160 μm correspond to the surface of the embryo for green, red, black and blue curves, respectively. Gray portion of each curve approximately corresponds to the motion of the droplet through the yolk whereas the remainder of the curve corresponds to movement through the cytoplasm layer. Fluctuations in the tracked bead position around t = 0 are due to unsteady motion of the microscope stage as magnet position was adjusted manually. If these fluctuations are disregarded, droplet behavior after removal of the magnet is essentially flat. In two of the four cases (the red and green traces), the directionality of the fluctuation is similar to that expected of recoil, but even if interpreted as such, the magnitude does not exceed 5 microns which is much smaller than the 30-micron displacement of the droplet through the cytoplasmic layer.