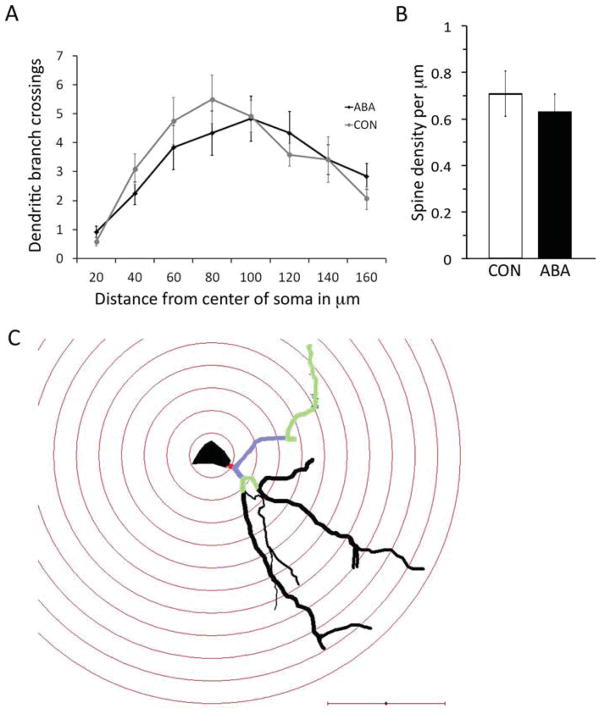
Fig. 8.
Effects of four days of ABA treatment on densely spiny, pyramidal-like neurons in the amygdala. Four neurons from each of the three animals per group were analyzed. Panel A shows the number of branches of the apical dendrite along its length. There was no statistically significant difference between the branching of the ABA and CON neurons by t-test. Panel B shows the spine density of a tertiary branch of the apical dendrite of three neurons from each of three animals per group. ABA and CON showed no difference in the spine density by t-test. Error bars denote standard error of the mean. Panel C shows a neuron traced under the light microscope with concentric spheres centered on the soma as a 3D reconstruction using Neurolucida software. The dendritic arbor was characterized by the intersections it makes with each concentric sphere. The primary dendrite is colored red, the secondary dendrites purple, and tertiary dendrites green. The tertiary dendrite was also used for tracing spines to measure spine density. Scale bar = 50 μm.