Table 1.
Structure-activity relationships on the aniline ring.
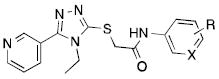
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmpd | R | X | EC50 (μM)a | % VUAA1 efficacyb |
| 6a (VUAA1) | 4-ethyl | H | 35.1 | 100 % |
| 6b | 3-ethyl | H | - | No agonism |
| 6c | 4-methyl | H | - | No agonism |
| 6d | 4-propyl | H | 94.1 | 57 % |
| 6e | 4-butyl | H | - | No agonism |
| 6f | 4-isopropyl | H | 11.7 | 127 % |
| 6g | 4-tertbutyl | H | LA d | 42 % d |
| 6h | 4-acetyl | H | 84.7 | 96 % |
| 6i | 4-methoxy | H | - | No agonism |
| 6j | 4-bromo | H | - | No agonism |
| 6k | 4-vinyl | H | 102 | 57 % |
| 6l | 4-ethynyl | H | - | No agonism |
| 6m | 2-methyl-4-ethyl | H | - | No agonism |
| 6n | 2-bromo-4-ethyl | H | - | No agonism |
| 6o | cyclohexylc | - | - | No agonism |
| 6p | 4-ethyl | N | - | No agonism |
Mean result of 4 experiments.
Maximum agonism of the compound, normalized to the activity of VUAA1.
Entire ring replaced.
LA = Low agonism. Compound shows agonism only at the highest concentration tested, but no EC50 could be calculated. Maximum observed agonism, but from an incomplete curve.
