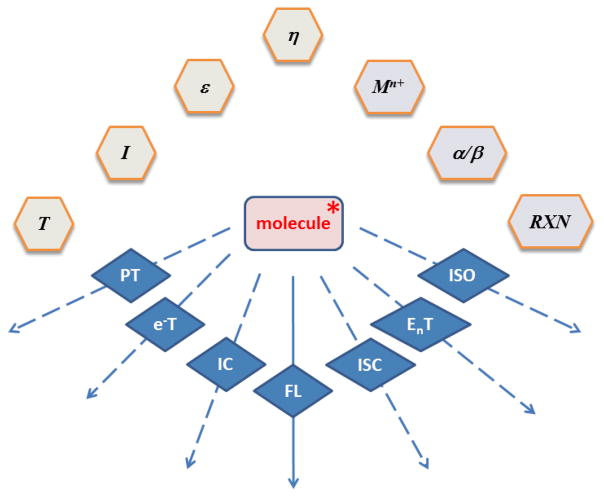
Fig. 1.
Relaxation pathways of an organic singlet excited state (molecule*), and factors that affect the rates of these pathways. Environmental factors and specific molecular interactions are shaded light gray and light purple, respectively. Factors: T – temperature; I – ionic strength; ε - dielectric constant; η - viscosity; Mn+ - metal ion; α – hydrogen bond donor; β - hydrogen bond acceptor; RXN – chemical reaction. Pathways: PT – proton transfer; e−T – electron transfer; IC – internal conversion; FL – fluorescence; ISC – intersystem crossing; EnT – energy transfer; ISO – (photo)isomerization.