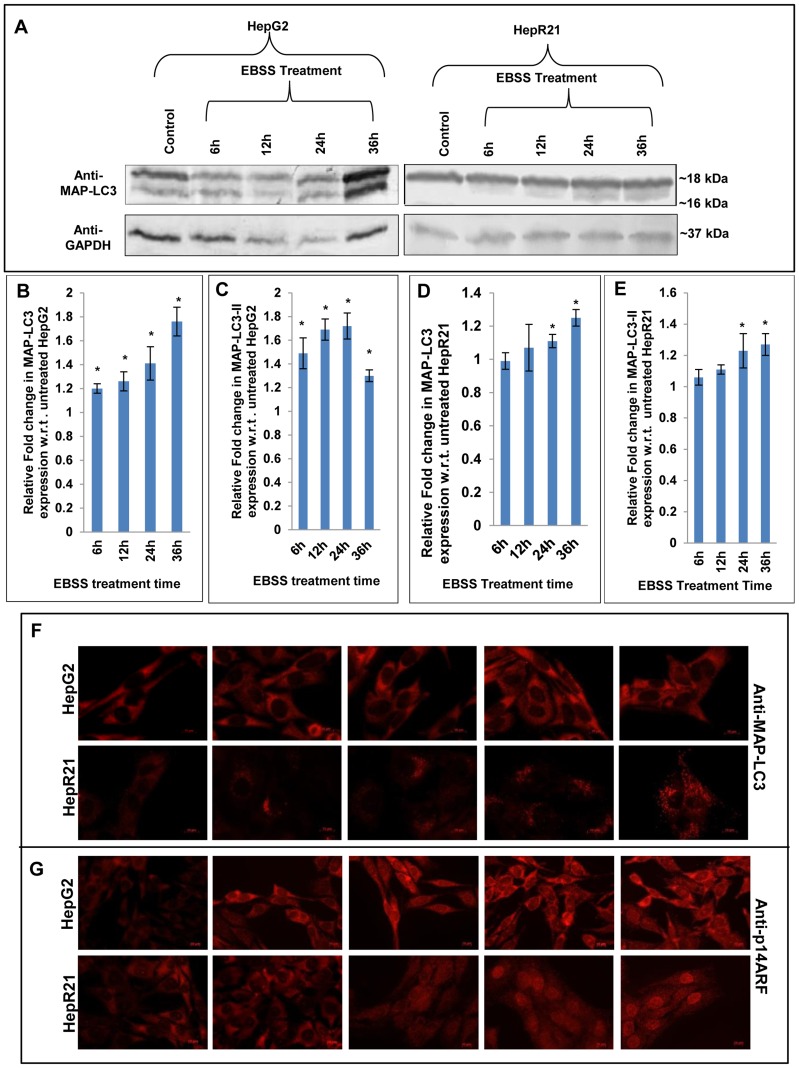
Figure 7. Upregulated MAP-LC3-II, differential expression and localization of tumor suppressor p14ARF in HepG2 unlike HepR21 upon nutrient deprivation.
[A-E] Elevated levels of total MAP-LC3 and MAPLC3-II in HepG2 upon nutrient starvation — After the aforementioned treatment with EBSS, the HepG2 and HepR21 cell lysates were immunoblotted with MAP-LC3 (1∶1000) and GAPDH (1∶20,000) antibodies. The fold change in expression of MAP-LC3 was calculated after normalization with GAPDH expression by IMAGE J and subsequently analyzed using ANOVA and represented in the graph as mean ± SD. The analysis showed a progressively increased expression of total MAP-LC3 in HepG2 along with increased period of starvation, significant for all the treatments compared to the untreated HepG2 cells. The expression of MAP-LC3-II (16 kDa), the lipidated form of MAP-LC3, indicative of the amount of autophagy taking place, was also found to be significantly upregulated for the abovementioned exposure to EBSS in HepG2 cells. Statistical analysis revealed a significantly increased expression of total MAP-LC3 and MAP-LC3-II only after 24 h of nutrient starvation in HepR21 cells (*p<0.05, n = 3). [F] Cytochemical expression of autophagic marker MAP-LC3 upon nutrient starvation — As observed in the immunoblot, an augmented expression of the autophagic marker MAP-LC3 was observed in HepG2 cells by sequential probing with anti-MAP-LC3, anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 546 and DAPI on fixed, treated and untreated cells. While the HepR21 cells showed the characteristic punctate staining throughout with only a slight rise after prolonged nutrient starvation. [G] Differential expression and localization of the tumor suppressor p14ARF observed for HepG2 and HepR21 — A comparative immunocytochemical analysis of the expression of the tumor suppressor protein, p14ARF in HepG2 and HepR21 indicated an elevated expression with the increase in period of nutrient deprivation in both the cell lines, more prominently in HepG2. Interestingly, a prominent differential localization of the protein in the two cell lines was also noticed. While the protein was predominantly expressed in the cytoplasm in HepG2 cells, it was observed to be translocated to the nucleus progressively with nutrient deprivation in case of HepR21 cells.