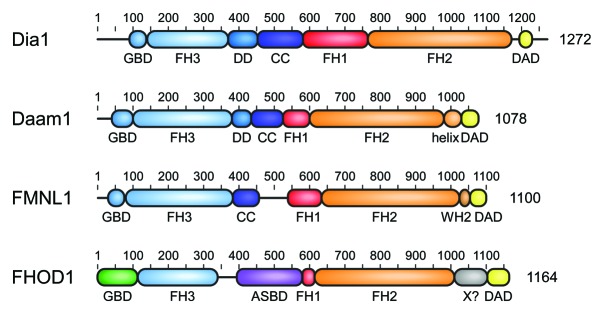
Figure 1. Domain architecture of mammalian Diaphanous-related formins. The multidomain proteins comprising more than 1000 amino acids contain a central proline rich FH1 domain followed by the actin polymerizing FH2 domain. DRFs contain in addition a C-terminal DAD autoregulation domain that interacts in the autoinhibited state with its N-terminal FH3 recognition domain. Additional dimerization elements DD (dimerization domain) and CC (coiled coil) contribute to the overall structure assembly of the formins. DRF activation occurs through interaction of the N-terminal GTPase-binding domain (GBD) with a Rho GTPase. Additional elements as the WH2 motif in FMNLs or the actin side-binding domain (ASBD) in FHOD1 contribute to the specificity of each DRF family.
