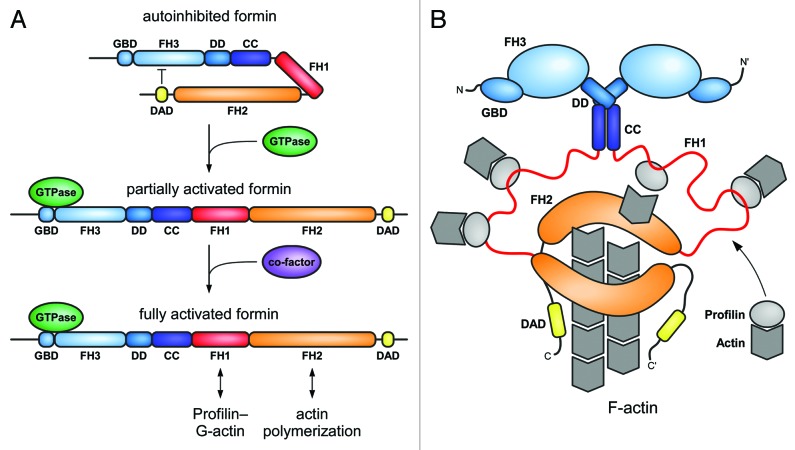
Figure 2. Cartoon of the regulation of a Diaphanous related formin. (A) In the autoinhibited state, the C-terminal DAD interacts with the N-terminal FH3 domain. Binding to a GTP-bound Rho GTPase leads to relief of the autoinhibited state by a partial displacement of the DAD and formin activation. Possible co-factors as e.g., kinases for formin phosphorylation, additional interaction factors of the DAD (as described for Daam), or interactions with membrane compartments for proper orientation might be required for full activation of the formin. GBD, GTPase-binding domain, FH1/2/3, formin-homology domains, DD, dimerization domain, CC, coiled coil domain, DAD, Diaphanous-autoregulation domain. (B) Cartoon of the activated formin dimer. The proline-rich FH1 domain recruits profilin–actin complexes in close proximity to the FH2 domain. G-actin molecules are polymerized to F-actin by the dimeric FH2 domain.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.