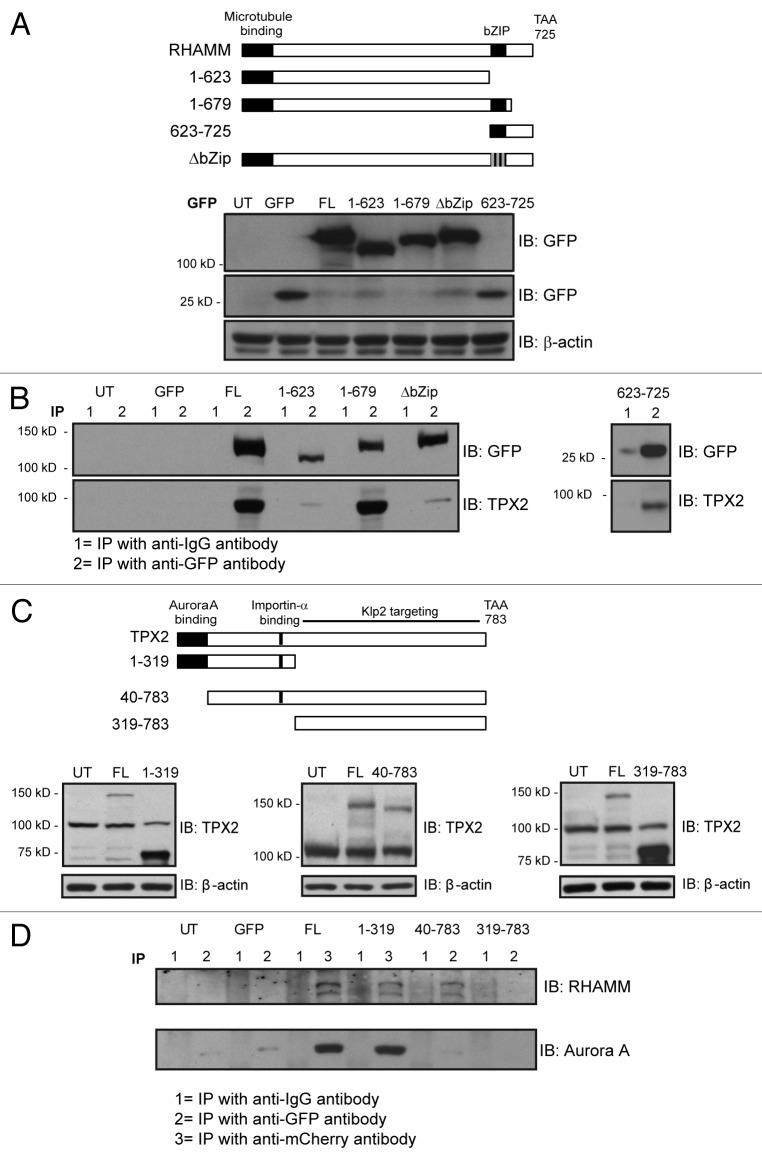
Figure 4. Characterization of the functional domains involved in RHAMM-TPX2 interaction during early mitosis. (A) Schematic diagram of defined domains in RHAMM. The 3 gray lines in the ΔbZIP construct represent leucines mutated to arginines. Western blot analysis confirmed the expression of GFP-RHAMM constructs. β-actin levels confirmed equal loading. (B) Immunoprecipitation of GFP-RHAMM constructs identified the bZIP motif as a necessary domain in RHAMM for the co-precipitation of TPX2. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with either an IgG control antibody (lanes marked 1) or antibodies against eGFP (lanes marked 2). (C) Schematic diagram of defined domains in TPX2. Western blot analysis confirmed the expression of mCherry-TPX2 and TPX2-GFP truncation variants. β-actin levels confirmed equal loading. (D) Immunoprecipitation of mCherry–TPX2 or TPX2–GFP truncation variants identified amino acids 40–319 as necessary for the co-precipitation of RHAMM. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with either an IgG control antibody (lane marked 1) or antibodies against eGFP (lane marked 2) or mCherry (lane marked 3).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.