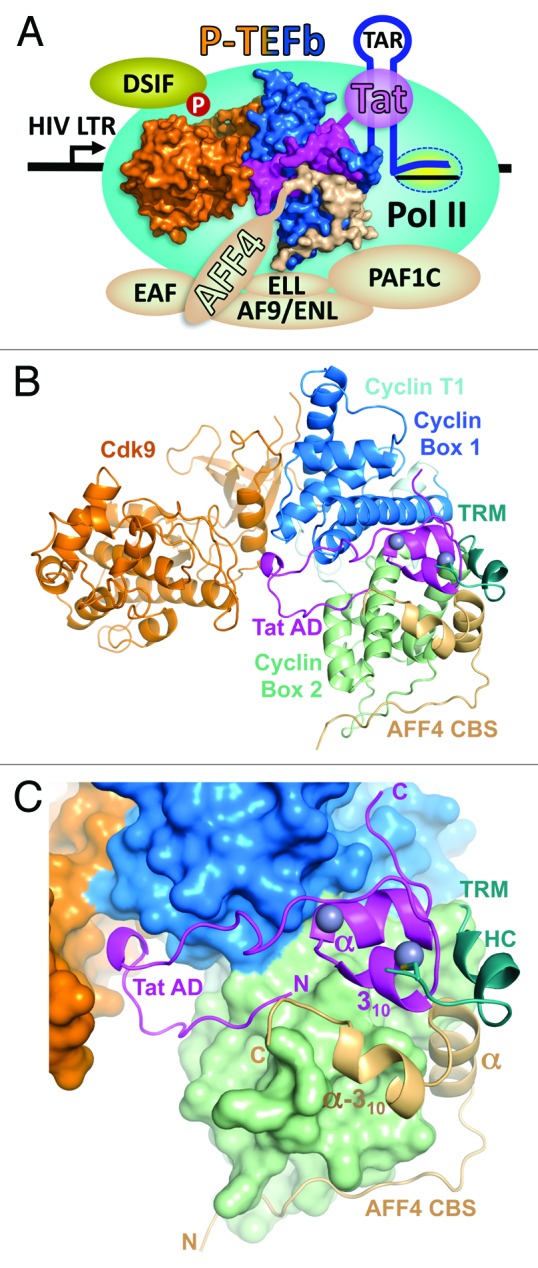
Figure 1. Overall view of Tat•AFF4•P-TEFb complex. (A) Functional context of the Tat•AFF4•P-TEFb complex. P-TEFb comprised of Cdk9 (orange) and Cyclin T1 (blue) provides a platform for the docking of HIV-1 Tat (magenta) and the AFF4 subunit (beige) of the super elongation complex (SEC). The SEC has 1 of each of these proteins: AFF1/4, EAF1/2, ELL1/2/3, and AF9/ENL. The nascent transcript (TAR) synthesized by Pol II engaged in the HIV LTR interacts with the RNA binding domain of HIV-1 viral protein Tat. Tat binds to Cyclin T1 and the N-terminus of the AFF4 subunit of the SEC which interacts with the PAF1 complex (PAF1C). PAF1C associates with Pol II further stabilizing the interaction of P-TEFb with the transcription complex. P-TEFb phosphorylates DSIF causing the transition into productive elongation and the synthesis of HIV mRNAs. (B) Cartoon representation of Tat•AFF4•P-TEFb complex. (C) A close-up view of activation domain (AD) of Tat and AFF4 CBS positioning on the surface of P-TEFb. In panel (B) the TRM of Cyclin T1 is drawn as cartoon and was not included in calculation of P-TEFb surface. Zinc ions of Tat are drawn as balls.
