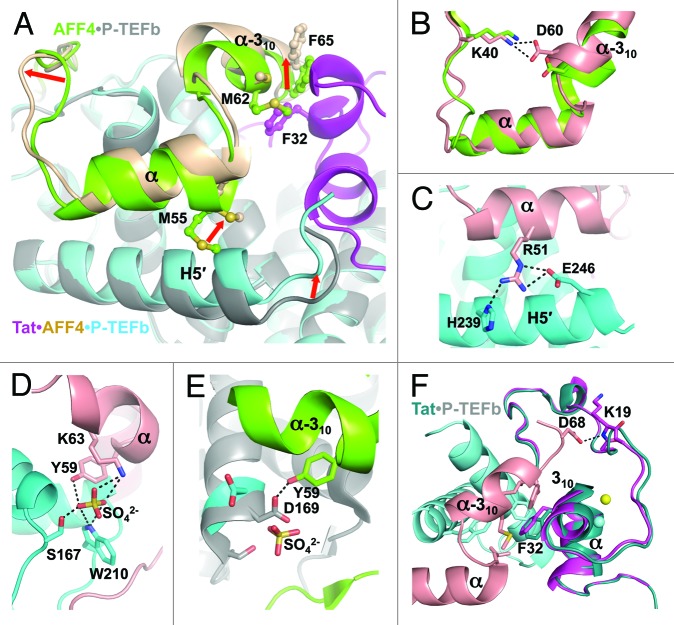
Figure 2. Structural changes induced by Tat binding to AFF4•P-TEFb or AFF4 binding to Tat•P-TEFb. (A) AFF4 structural changes induced by Tat binding to AFF4•P-TEFb. Red arrows indicate the directions of shifts in AFF4. (B) Tat binding results in closer positioning of AFF4 Lys40 and Asp60 side chains enabling the formation of H-bond. (C) H-bonds between AFF4 and Cyclin T1 that present in Tat•AFF4•P-TEFb structure and absent in structure of AFF4•P-TEFb. (D) Sulfate-mediated H-bonds between AFF4 and Cyclin T1 in the structure of Tat•AFF4•P-TEFb. (E) H-bond between AFF4 Tyr59 and Cyclin T1 Asp169 in the structure of AFF4•P-TEFb that is substituted by sulfate-mediated H-bonds in Tat•AFF4•P-TEFb. For the comparison, the locations of sulfate ion and Asp169 from the superimposed structure of Tat•AFF4•P-TEFb are also shown. (F) Structural changes of Tat induced by AFF4 binding to Tat•P-TEFb.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.