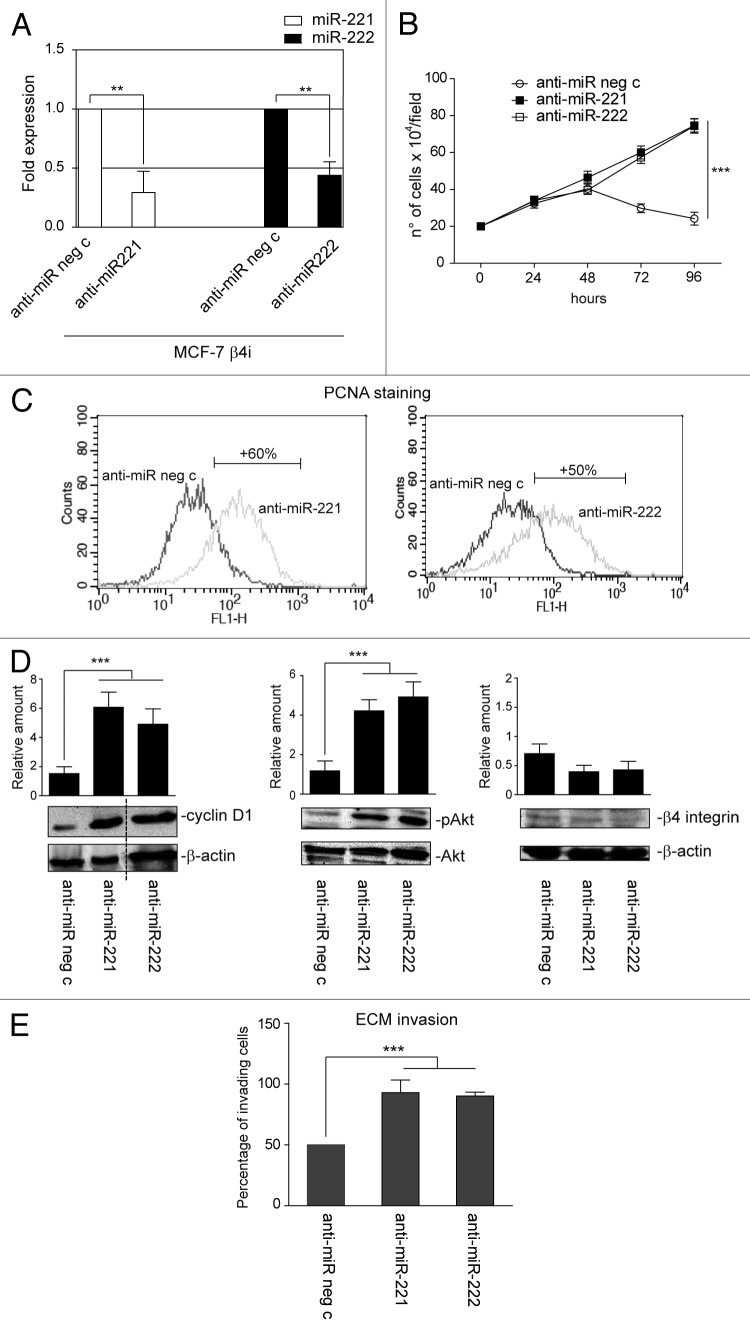
Figure 6. miR-221/222 loss-of-function in the MCF-7 β4i clone rescues proliferation and invasiveness. (A) qRT-PCR was performed to evaluate miR-221 and miR-222 expression in MCF-7 β4i cells transfected with anti-miR neg c or anti-miR-221 or anti-miR-222. The reported data are normalized to RNU6B and are representative of 5 experiments (n = 5) (**P < 0.01 miR-221 and miR-222 expression in MCF-7 β4i cells transfected with anti-miR-221/222 vs. cells transfected with anti-miR neg c). (B) A cell proliferation assay was performed for indicated time intervals on MCF-7 β4i cells transfected with anti-miR neg c, anti-miR-221, or anti-miR-222 (***P < 0.001, anti-miR-221 or anti-miR-222 vs. anti-miR neg c transfected MCF-7 β4i cells) (n = 3). (C) PCNA staining in MCF-7 β4i cells transfected as above. Percentage ± SEM of increased proliferation: anti-miR-221, 60 ± 3.7; anti-miR-222, 50 ± 4.2 ***P < 0.001. (D) MCF-7 β4i cells, treated as above, were analyzed for cyclin D1, pAkt, and β4 integrin content. Protein levels were normalized to β actin or Akt content. The results are representative of 3 different experiments, performed in triplicate (n = 3) (***P < 0.001 anti-miR-221 and anti-miR-222 vs. anti-miR neg c for cyclin D1 and pAkt content). (E) An invasion assay was performed on MCF-7 β4i cells treated as indicated. Percentage of invading cells is reported (***P < 0.001 anti-miR-221 and anti-miR-222 vs. anti-miR neg c) (n = 4).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.