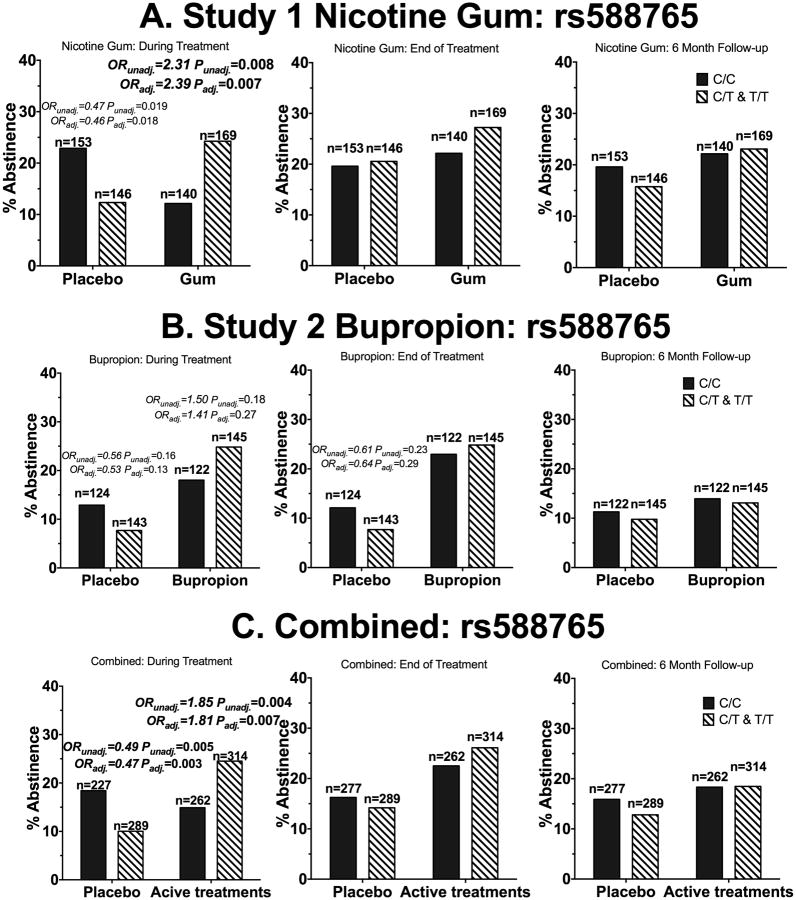
Figure 3.
The ‘T’ allele of rs588765 was associated with smoking abstinence in African American smokers receiving active pharmacological treatment. A) Participants in who received nicotine gum or placebo (Study 1). B) Participants who received active bupropion or placebo (Study 2). C) Participants who received active pharmacological treatments (combined analysis). ORunadj. = unadjusted odds ratio of quitting for the CT&TT genotype group compared to the CC genotype. ORadj.= odds ratio of quitting for the CT&TT genotype group compared to the CC genotype after adjusting for age, sex, baseline CPD, menthol status and type of counseling sessions. There was also a significant treatment (combined active vs. combined placebo) by rs588765 genotype interaction during treatment (OR=3.75, P<0.001). The OR and P-values are shown for all comparisons with ORs smaller than 0.7 or greater than 1.4. P-values below 0.0125 were considered statistically significant due to multiple comparison adjustments. Statistically significant values are bolded. N represents the number of participants.