Figure 6.
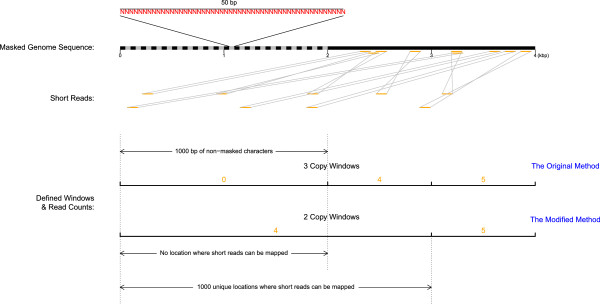
Illustration of the modified method of windows definition. As showed in the top of the graph, on a 4 kb genome sequence, black regions represent A/T/C/G characters and grey regions denote N characters. Due to hard masking, 50 bp N blocks are uniformly distributed on the first 2 kb sequence, resulting in no any 100 bp reads being mapped there. According to copy window definition by the original method that every 1,000 bp of non-masked characters are defined as one copy window, the whole 4 kb long masked genome sequence is divided into three copy windows and the first 2 kb long sequence is defined as one copy window. The three copy windows have read counts of 0, 4 and 5, respectively. Thus the hard masked sequence of the first 2 kb may be considered as deletion. In contrast, the modified method we proposed herein defines every 1,000 unique locations where short reads can be mapped as one copy window, so the masked genome sequence is accordingly divided into two copy windows with read counts of 4 and 5, respectively, avoiding false prediction of deletion for the hard masked region.
