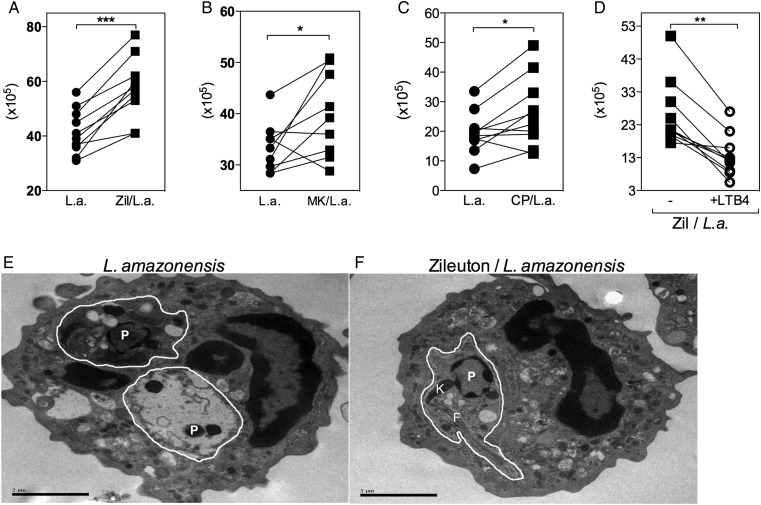
Figure 4.
Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase increases human neutrophil susceptibility to Leishmania amazonensis infection through the high-affinity leukotriene B4 (LTB4) receptor B leukotriene receptor 1 (BLT1). Human neutrophils were treated with 10 µM Zileuton (A), 10 µM MK886 (B), or 100 nM CP105969 (C) for 15 minutes prior to infection with L. amazonensis–GFP (1 neutrophil to 10 L. amazonensis). Exogenous LTB4 was added to selected cultures of Zileuton-treated neutrophils (D). After 3 hours of infection, cells were washed, fed with supplemented Schneider's medium, and cultured at 23°C for an additional 24 hours. Parasite viability was measured by assessing the number of extracellular motile promastigotes produced. Transmission electron microscopy was used to investigate ultrastructural morphological alterations in infected (E) and Zileuton-treated infected neutrophils (F). White lines delimit parasitophorous vacuoles. Parasites (P), kinetoplastids (K), and flagella (F) are indicated. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01; ***P ≤ .001.