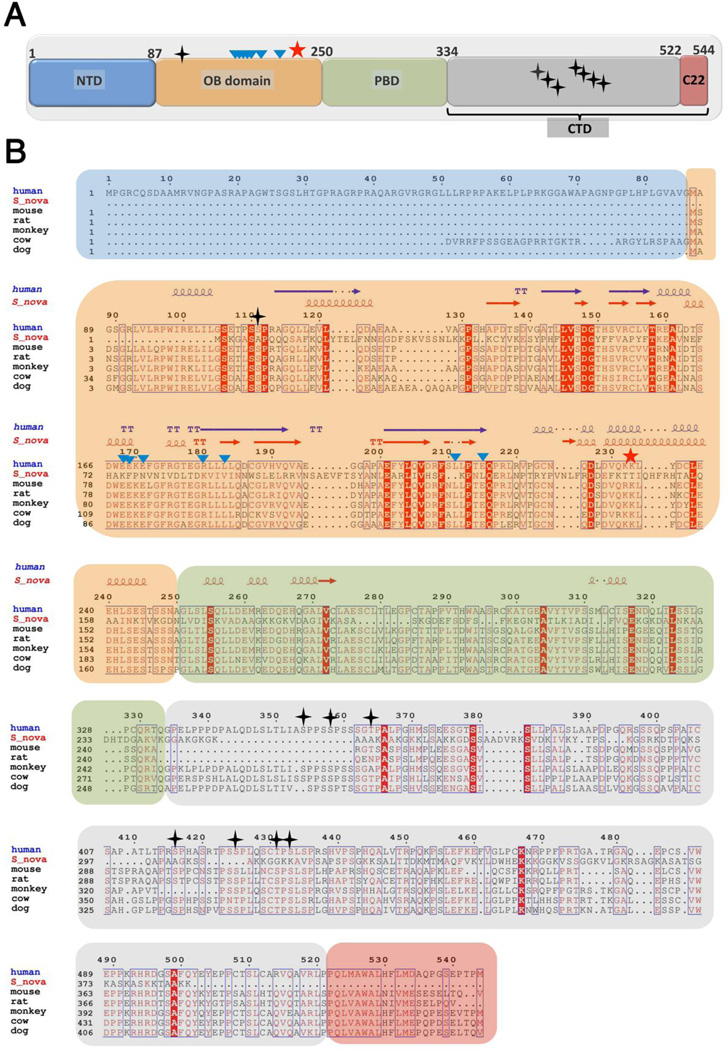
Figure 1.
Domain organization and sequence alignment of TPP1 proteins. (A) Cartoon schematic depicting the individual domains of TPP1. The first 86 residues of human TPP1 (NTD; blue) are not conserved. The 87–250 region contains the OB-fold domain (TPP1-OBD; orange). Residues 250–334 comprise the POT1-binding domain (PBD; green). There are multiple Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites within the C-terminal domain (CTD; 334–544aa; grey), while the last 22 residues (C22; red) are most critical for TIN2 interactions. Phosphorylation sites (S111 in OBD and seven in CTD) are highlighted with black-stars. The TEL patch residues involved in telomerase interaction are marked as teal-triangles. Lys233 has been shown to be ubiquitylated and is labeled as a red star. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of TPP1 with its homologs. The multiple sequence alignment was performed using Clustal-omega [101] and further formatted using Espript [102] to highlight sequence similarities and identities among the proteins. Symbols and protein domain colors are the same as described in panel (A). The secondary structural elements of human TPP1(87–250) and S.nova (1–222) are depicted above the sequence alignment.