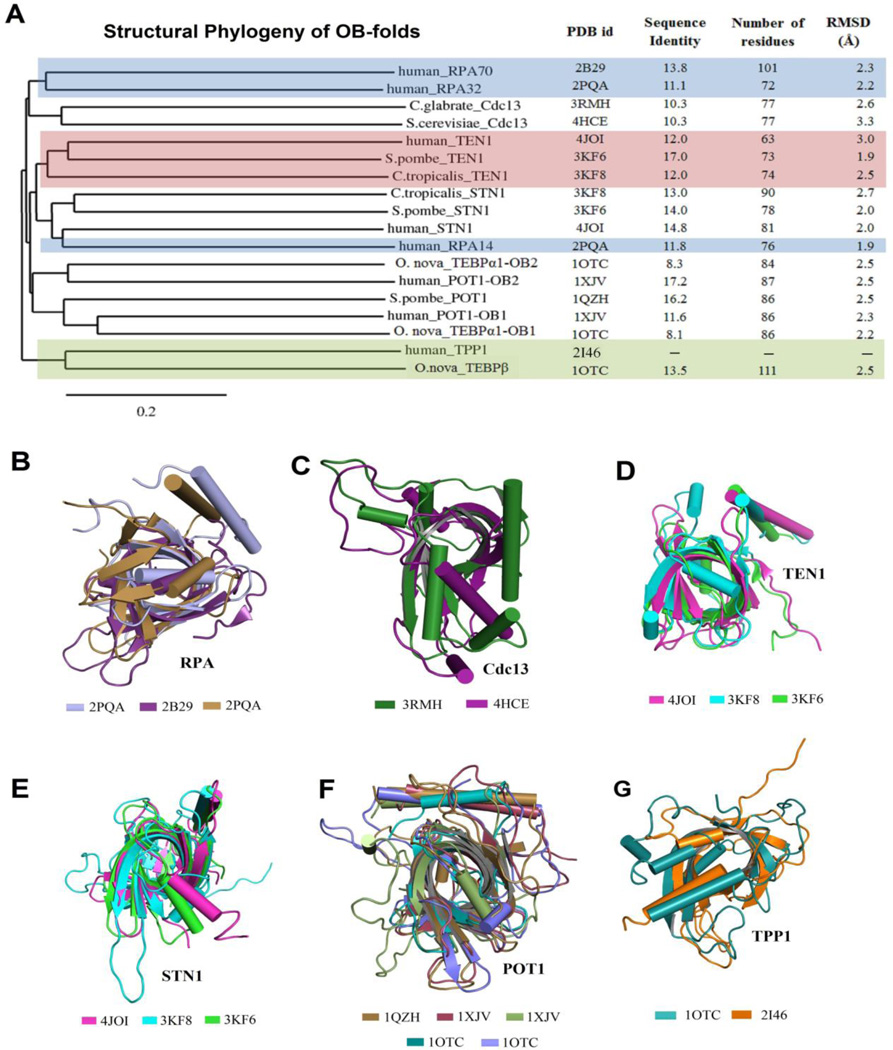
Figure 2.
The structure-based phylogenetic analysis of a representative list of OB-fold containing proteins that are involved in telomere maintenance. Proteins with OB-folds were selected based on telomere-related function and on their structural availability. (A) A three-dimensional structure based comparison was performed using STRAP (STRuctural Alignments of Proteins) to construct a phylogenetic tree based on structural conservation. The tree was constructed using ‘neighbor-joining’ clustering methods in ClustalW. The branches of the tree are labeled with the organism and protein name. The last column is a structural analysis (in terms of RMSD) comparing the structure of individual OB-domains with human TPP1-OBD. Phylogenetic analysis clustered the various proteins into the following families:(B) RPA, (C) Cdc13, (D) Ten1 domain, (E) Stn1 domain, (F) POT1, and (G) TPP1-like. The similarities in OB-fold architecture, as well as the helix orientation among members, are apparent in the superpositions of members in each family. Note that variations between families are restricted primarily to the loop and helix orientations on the perimeter of the OB-fold architecture. Protein database (PDB) accession numbers are listed below the appropriate structures.