Figure 1. Chemical modification of human neutrophil Cyt b with mass spectrometry compatible crosslinkers.
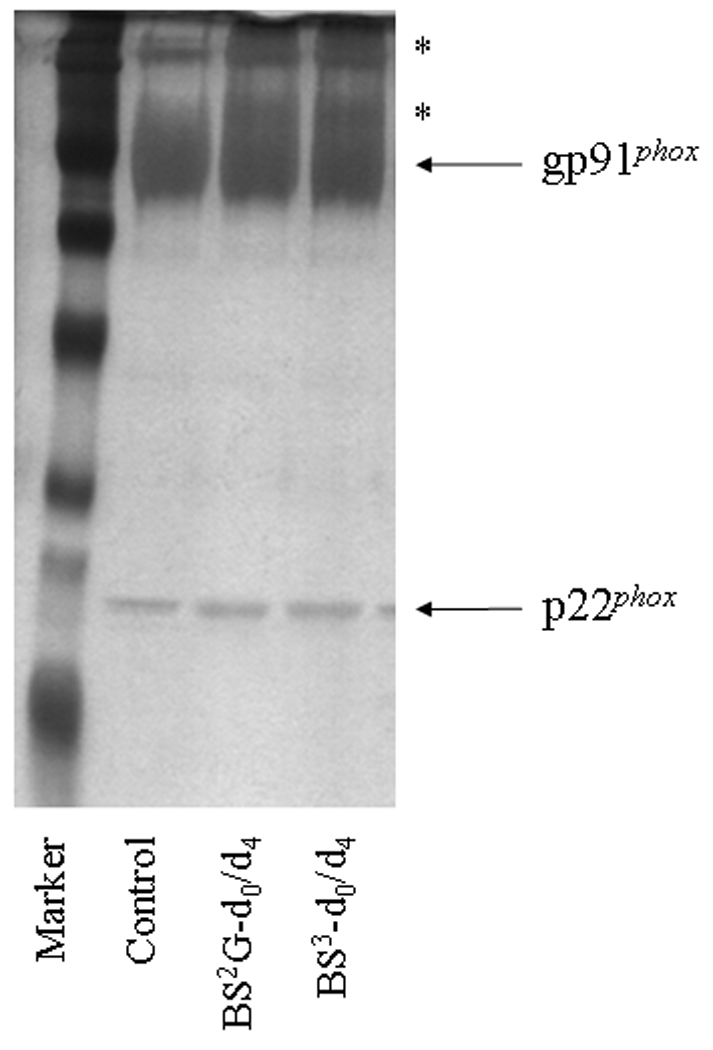
Following affinity purification of Cyt b from human neutrophil membrane fractions, chemical modification was carried out with homobifunctional, amine-reactive crosslinking agents BS2G-d0/d4 and BS3-d0/d4. In order to monitor crosslinking reactions, quenched samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and silver stained as follows: M, molecular weight standards; Control, Cyt b following incubation with 5% DMSO for 50 min at room temperature (control sample); BS2G-d0/d4, Cyt b following incubation with a 60-fold molar excess of BS2G-d0/d4 for 50 min at room temperature; and BS3-d0/d4, Cyt b following incubation with a 60-fold molar excess of BS3-d0/d4 for 50 min at room temperature. Asterisks (*) indicate higher molecular weight species that were shown contain both gp91phox and p22phox subunits by MALDI mass spectrometry (data not shown). Qualitatively similar results were obtained for all reaction conditions used in the present study.
