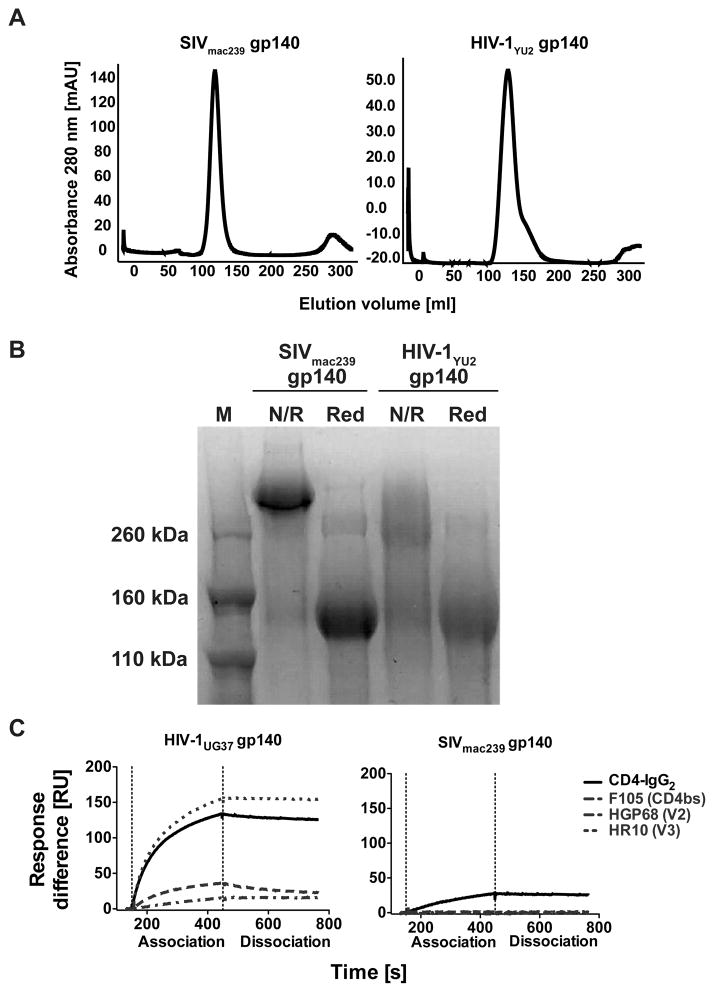
FIGURE 1. Trimerization of SIVmac239 gp140 and binding to human CD4.
A) Gelfiltration chromatography analysis of the soluble gp140 trimers from SIVmac239 and HIV-1YU2. Both complexes elute as a single symmetric peak at the expected elution volume for the trimeric species demonstrating that the gp140 trimers produced were pure and homogenous. The chromatography trace for HIVYU2 is representative for the different HIV-1 gp140 used in this study. B) Non-reducing (N/R) and reducing (Red) SDS PAGE analysis of SIVmac239 and HIV-1YU2 gp140. The SIVmac239 gp140 protein runs as a high molecular weight band under non-reducing conditions, indicating that the three polypeptides of the trimer are covalently linked by disulfide bonds between the three gp140 chains. HIV-1YU2 gp140 runs as a smear under non-reducing conditions suggesting that the three polypeptides of the trimer are not covalently linked. C) Surface plasmon resonance analysis of SIVmac239 gp140 and HIV-1 UG37 gp140 binding to human CD4 and anti-HIV-1 NAbs. SIVmac239 (right panel) or HIV-1UG37 (left panel) were immobilized and their binding to tetrameric soluble human CD4 (CD4-IgG2) as well as mAb F105, HGP68 and HR10 was measured.