Figure 4. MEK7 over-expression protects against LT-induced Ca2+idysregulation and PP2A activation.
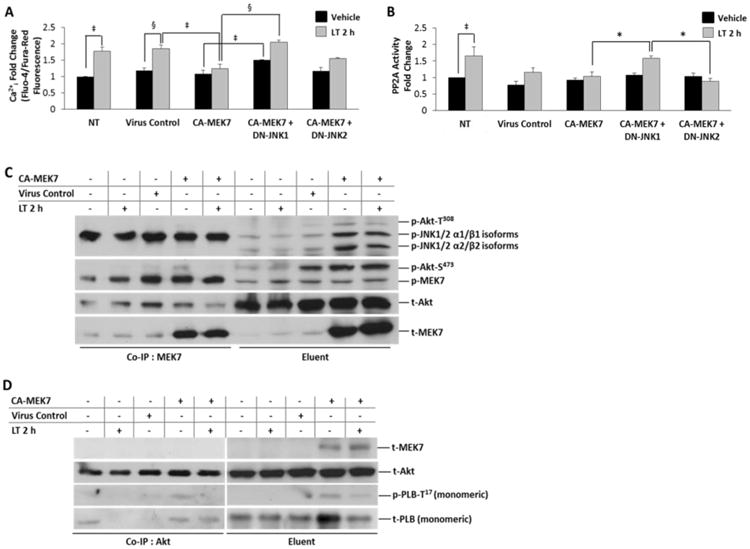
A, Ratiometric Ca2+i determination by Fluo-4/Fura-Red fluorescence, normalized to baseline fluorescence (dye only). NRVM were infected with the indicated adenoviral constructs (CA-MEK7, CA-MEK7+DN-JNK1 or CA-MEK7+DN-JNK2 for 36 h prior to either vehicle (distilled water) or 2 h LT (0.05 ng/mL PA + 0.025 ng/mL LF) treatment. Lysates harvested from NRVM infected with an empty expression vector were used as the virus control. B, Specific PP2A activity fold change represented as PP2A enzymatic activity/PP2Ac total protein. Adenovirus-infected NRVM were treated with either vehicle (distilled water) or LT (0.05 ng/mL PA + 0.025 ng/mL LF) 2 h prior to fluorometric determination of PP2A enzymatic activity. C, Co-immunoprecipitation of MEK7 with phosphorylated MEK7, JNK, Akt-T308 and Akt-S473 from NRVM lysates expressing CA-MEK7. Co-immunoprecipitated protein is shown at left, and the input lysate (eluent) is shown at right. D, Co-immunoprecipitation of p- PLB-T17 and t-Akt from NRVM lysates with anti-Akt (pan) antibody after expression of CA-MEK7 adenovirus. Co-immunoprecipitated protein is shown at left, and the input lysate (eluent) is shown at right. MEK7 protein is found in the lysate (eluent); CA-MEK7-induced p-PLB-T17/Akt interactions are revealed as co-immunoprecipitated (Co-IP) by Akt. N = 4.
