Figure 1.
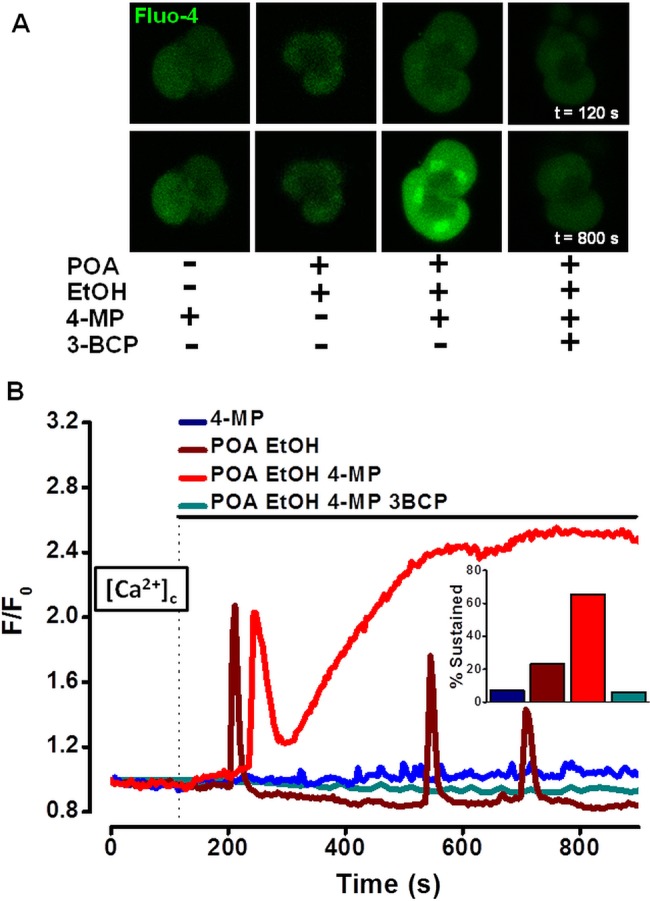
Effects of ethanol (EtOH), palmitoleic acid (POA), 4-methylpyrazole (4-MP) and 3-benzyl-6-chloro-2-pyrone (3-BCP) on [Ca2+]C in pancreatic acinar cells. (A) Typical fluorescence images showing changes of [Ca2+]C (Fluo4, green) before (t=120 s) and after (t=800 s) application of combinations of ethanol (10 mmol/L), POA (20 μmol/L), 4-MP (100 μmol/L) and 3-BCP (10 μmol/L). Addition of ethanol/POA/4-MP caused sustained elevation of [Ca2+]c seen at 800 s. (B) Combination of ethanol/POA (wine) induced predominantly oscillatory increases of [Ca2+]C, while additional presence of 4-MP (100 μmol/L) promoted a shift towards sustained increases (red); 4-MP alone was without effect (blue). The addition of 3-BCP abolished sustained rises induced by ethanol/POA/4-MP (cyan). Cumulative data expressed as percentage of cells exhibiting sustained rises (inset) (F/F0=>1.5) at 800 s (total n=159 cells).
