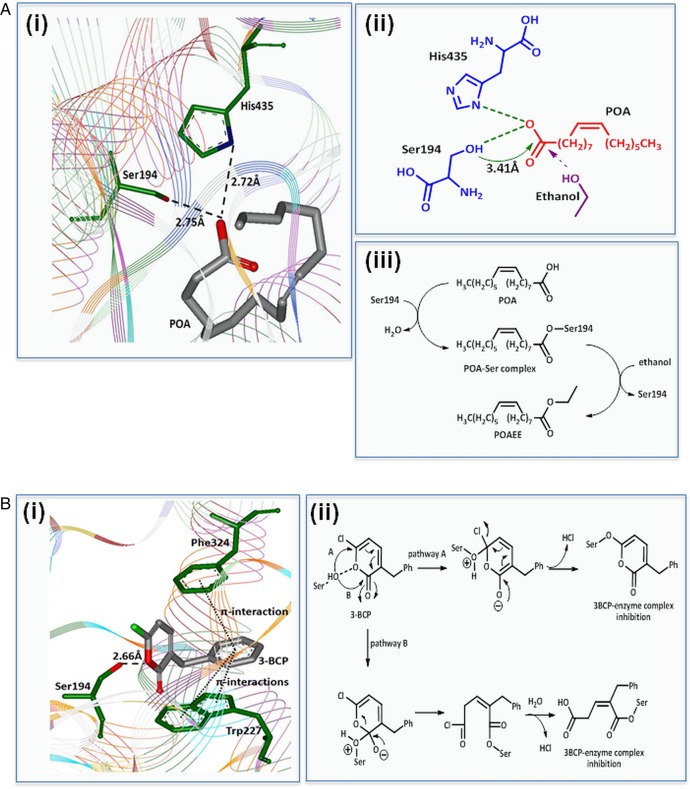
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanism of fatty acid ethyl ester (FAEE) generation by carboxylester lipase (CEL) and inhibition by 3-benzyl-6-chloro-2-pyrone (3-BCP). (A) (i) Molecular docking interactions predict binding of palmitoleic acid (POA) in the active site of CEL via interaction with Ser194 and His435 residues suggesting feasibility of mechanism-based esterification. (ii) 2D representation of the binding mode of POA in the active site indicates that the Ser194 hydroxyl group can react with the POA carbonyl group to afford a POA-Ser complex; ethanol easily displaces Ser from the complex forming POA ethyl ester (POAEE). (iii) Mechanism-based esterification of POA to POAEE. (B) (i) Binding of 3-BCP in CEL active site indicates interaction with Ser194 (via hydrogen bonding), further stabilised by two π-interactions with Phe324 and Trp227. (ii) Mechanism-based reaction of 3-BCP with Ser194 residue resulting in formation of 3-BCP-enzyme complex which is inhibitory for FAEE formation.